Fig. 6.
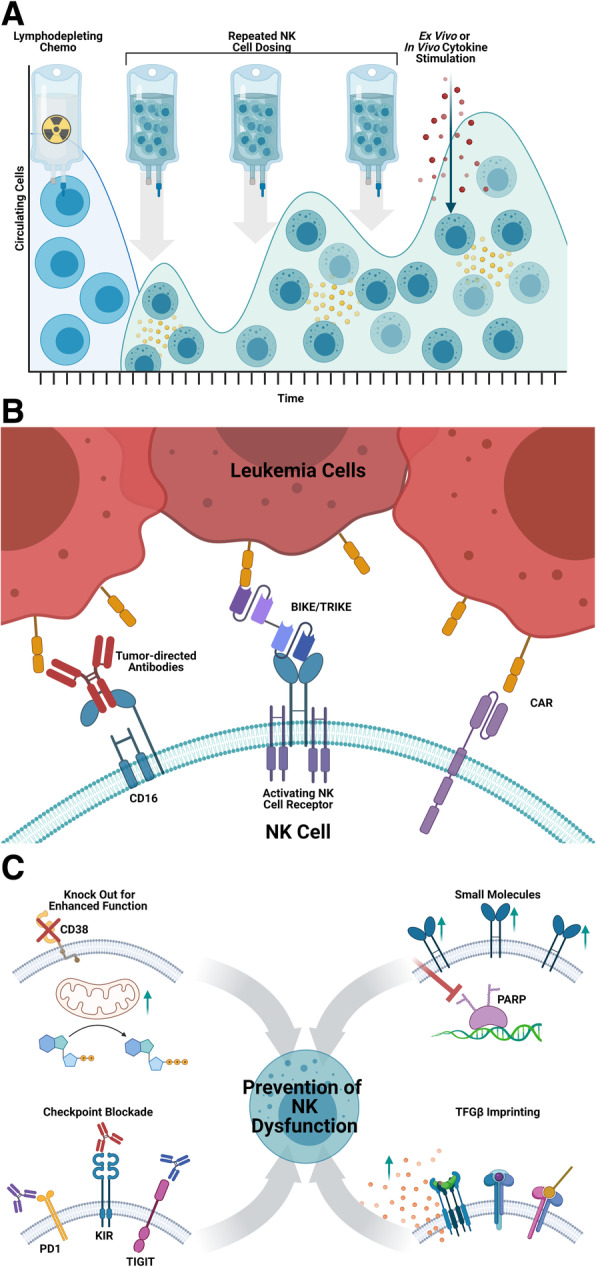
NK cell therapy barriers and solutions. a Strategies to improve in vivo persistence of adoptive NK cells include use of lymphodepleting chemotherapy, repeated NK cell doses, exogenous cytokine stimulation, and cytokine secreting “armored” NK cells. b Tumor cell immune evasion can be overcome by antibodies directed at the tumor antigen to encourage NK cell ADCC, bispecific engagers interacting with NK activating receptors, or engineered chimeric antigen receptors. c Strategies to decrease immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment include (clockwise from the top left) genetic knock out/in of proteins to enhance NK function (ex. CD38 knock out), small molecule inhibitors or immunomodulatory drugs (ex. PARP inhibitors to upregulate NK activating receptors), priming the NK cells ex vivo for preservation of function in vivo (ex. TGFβ imprinting preserving cytolysis and cytokine secretion upon re-exposure to TGF β in the TME), and checkpoint blockade
