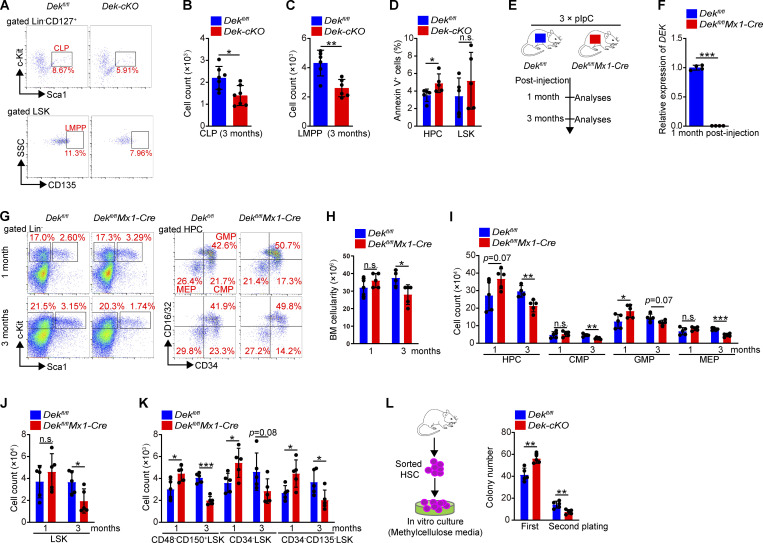
Figure S2.
DEK deletion decreases the HSPC pool in mice. (A) FACS analysis of CLPs (Lin−CD127+Sca-1loc-Kitlo) and LMPPs (Lin− Sca-1+c-Kit+CD135+) in BM cells of Dekfl/fl and Dek-cKO mice. (B and C) Count of CLPs and LMPPs in BM cells of Dekfl/fl and Dek-cKO at 3 mo of age (n = 6–7). (D) Analysis of apoptotic HPCs and LSK cells in BM cells of Dekfl/fl and Dek-cKO at 3 mo of age. Annexin V+ cells represent early and later apoptotic cells (n = 5). (E) Experimental schematic for the generation of mice with inducible deletion of DEK, Dekfl/flMx1-Cre. Mice were treated with an i.p. injection of 10 µg pIpC per gram of body weight every second day for a total of three injections. The mice were sacrificed for analyses at 1 or 3 mo after pIpC injection. (F) Relative mRNA expression of DEK in freshly sorted HSCs of Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre mice at 1 mo after pIpC injection (n = 4). (G) FACS analysis of LSK cells and HPCs in Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre BM cells at 1 or 3 mo after pIpC injection. (H) BM cells count of Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre mice after pIpC injection (n = 5). (I) Count of HPC, CMP, GMP, and MEP in BM cells of Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre mice after pIpC injection (n = 5). (J) LSK cells count in Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre BM cells (n = 5). (K) HSC (CD48−CD150+LSK, CD34−LSK, or CD34−CD135−LSK) count in Dekfl/fl and Dekfl/flMx1-Cre BM cells (n = 5). (L) In vitro assay of the CFUs at 10–12 d after plating Dekfl/fl and Dek-cKO HSC cells. For the second plating, live cells from the colonies obtained during the first plating were plated as before and cultured for 10–12 d (n = 5). Error bars represent means ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; Student’s t test. Data are representative of three independent experiments.