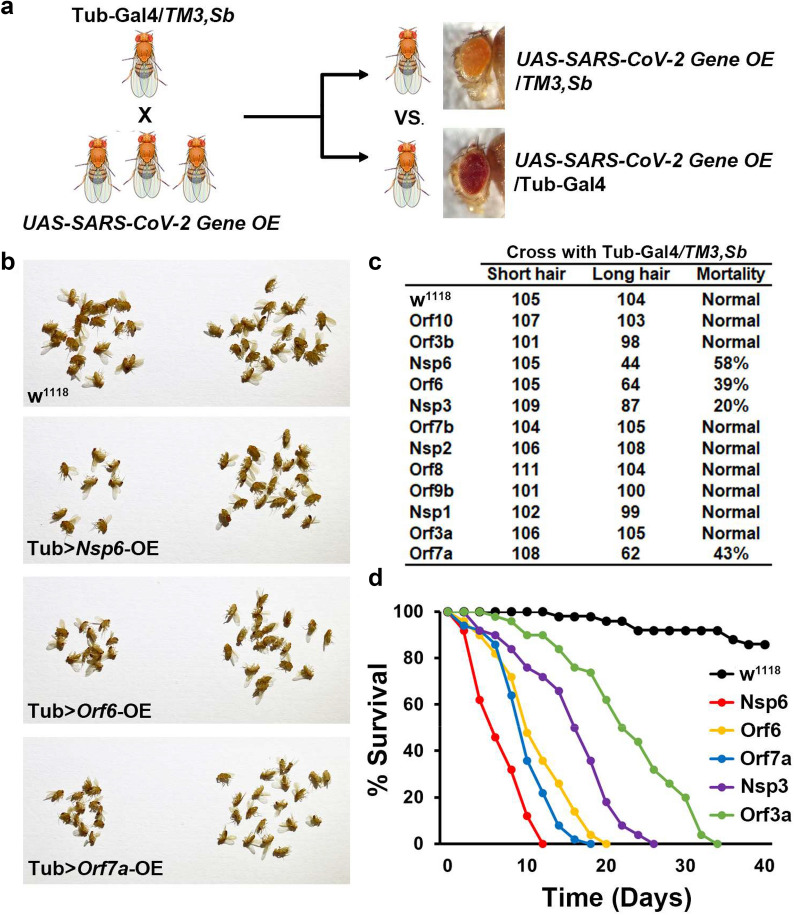
Fig. 2.
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6, Orf6 and Orf7a transgene expression causes developmental lethality. a Schematic representation of genetic screen to identify individual SARS-CoV-2 genes with pathogenic effect. b Images of adult progeny emerging from pupa stage from cross in a, distinguished by carrying the balancer (TM3, Sb; orange eyes and short hair on back; no viral transgene expression) or with expression of the SARS-CoV-2 gene driven by the ubiquitous Tubulin (Tub) enhancer (red eyes and long hair). w1118 is a wild type control. c Quantification of mortality rate prior to eclosion for the individually expressed SARS-CoV-2 genes from the cross in a. Mortality calculated as: (long hair − short hair) / short hair × 100. d Graph displaying lifespan data for adult flies carrying SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6, Orf6, Orf7a, Nsp3 or Orf3a transgenes. w1118 is a wild type control. N = 100 flies per group. Abbreviations: E, envelope protein; M, membrane protein; N, nucleocapsid protein; Nsp, non-structural protein; OE, overexpression; Orf, accessory protein; S, spike protein; Sb, stubble TM3, chromosome 3