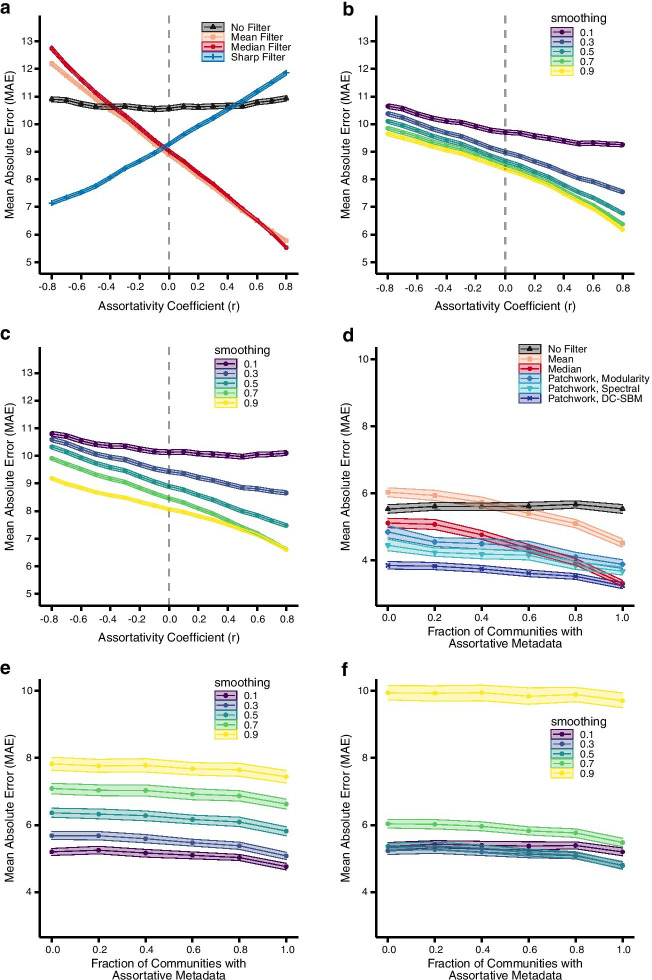
Fig. 2.
Filter performance on synthetic networks. Network filter tests on synthetic graphs with varying structures and known noise. The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of a network filters, b Laplacian exponential diffusion kernel, and c netSmooth on the permuted nodes as a function of the assortativty coefficient of 5000 instances of noisy non-modular graphs. The smooth filters (mean and median) perform best on assortative data (), while the sharp filter is optimal for disassortative data (). When data are neither assortative nor disassortative (), netSmooth and Laplacian exponential kernels perform best. The MAE of d network filters, e Laplacian exponential diffusion kernel, and f netSmooth on the permuted nodes as a function of the fraction of communities with assortative data values for 100 instances of noisy modular graphs. Each network instance has 5 communities and we vary how many communities have assortative versus disassortative data values with a moderate assortativity coefficient . The shaded areas indicate 99% bootstrapped confidence intervals