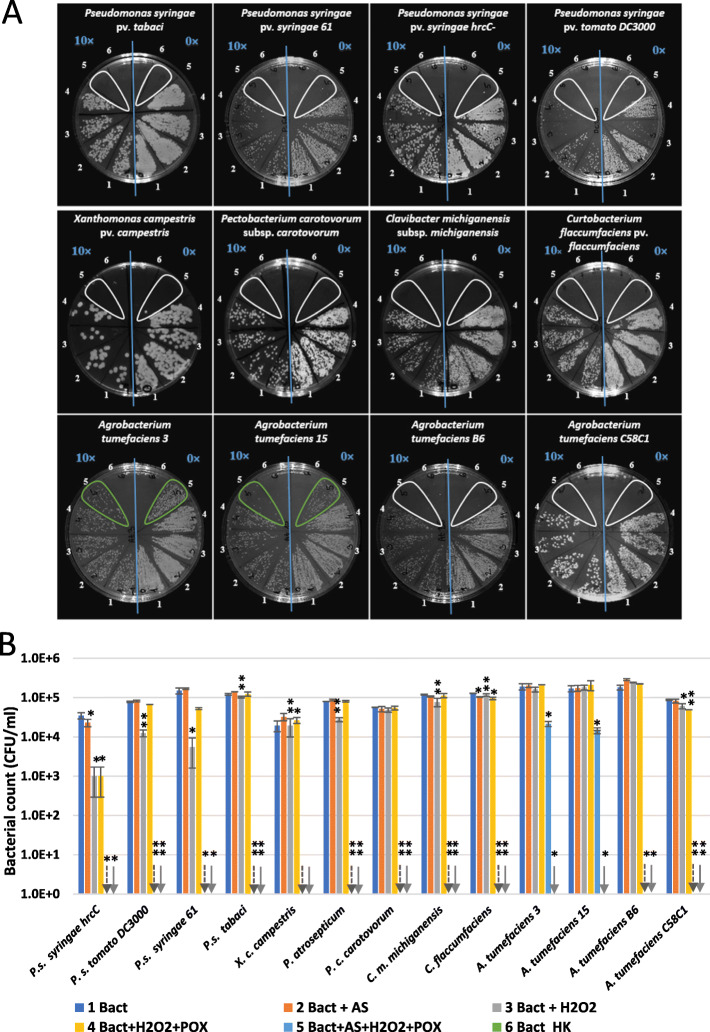
Fig. 3.
Antimicrobial effect of oxidized form of acetosyringone on different plant pathogenic bacteria. Bacteria (105 CFU/ml) were added to reaction mixtures containing 50 μM AS, 50 μM H2O2, and 0.72 U/ml horseradish peroxidase, and various control mixtures from which one or two components were omitted. Serial dilutions were plated following 3 h of co-incubation for CFU determination. a Typical representative examples of serial dilutions plated on Kings’s B agar plates. Right half of each plate: no dilution (0×), left side of each plate: 10× dilution (indicated with blue lettering). Numbering of treatment combinations applied to the bacterial suspensions: 1. non-treated control; 2. AS; 3. H2O2; 4. H2O2 + POX; 5. AS + H2O2 + POX; 6. HK. b Diagram showing quantification of the results. Error bars indicate standard deviations. Asterisks indicate significant difference from corresponding water-treated controls according to student’s T-test (*p < 0.1; **p < 0.05). Downward arrows indicate zero values. Abbreviations: Bact: bacterium, AS: acetosyringone, HK: heat-killed, POX: horseradish peroxidase