Figure 5.
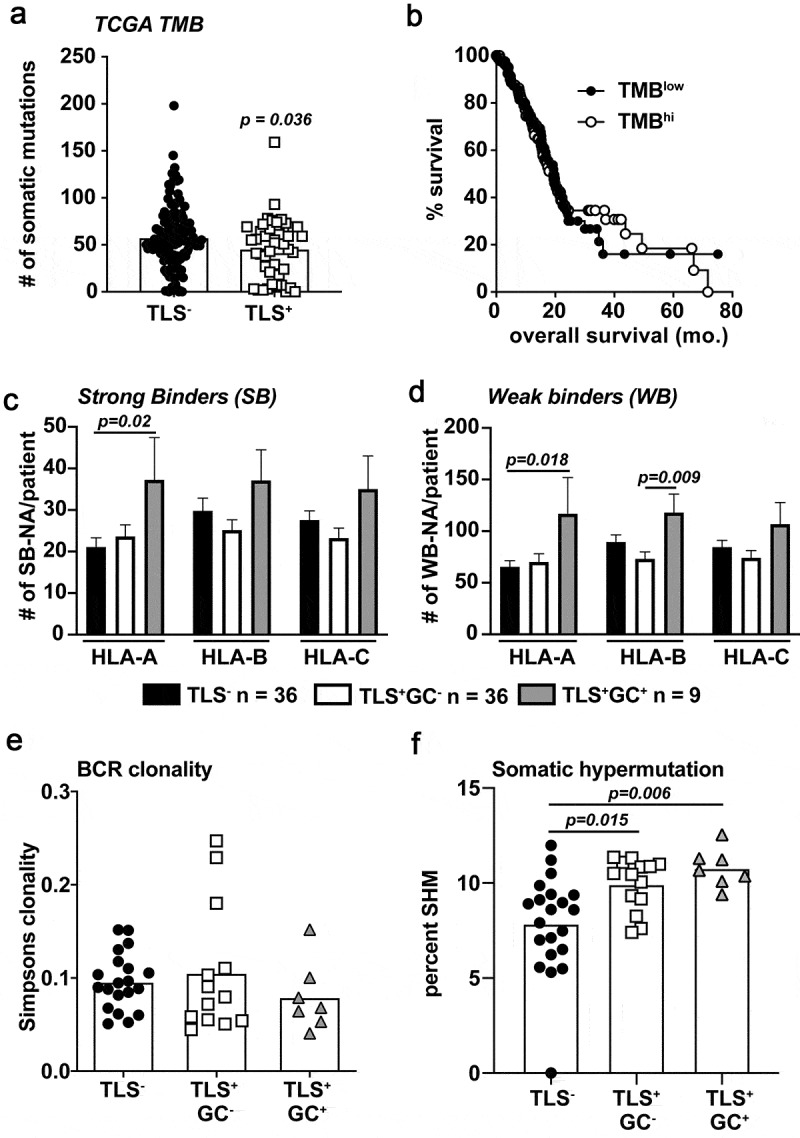
Predicted HLA binding neoantigens are increased in M-TLS+ PDAC patients accompanied by increased rates of B cell somatic hypermutation. A) TCGA tumor mutation burden between TLS− and TLS+ patients from the TCGA-PAAD dataset. B) Kaplan-Meier curve of TMBhi vs. TMBlow determined on a mean cut-point was used to stratify TCGA-PAAD patients for overall survival. C) Predicted strong binding (rank<0.5%) neoantigens/patient partitioned into HLA-A, B, and C specific peptides using a proprietary neoantigen prediction pipeline in conjunction with HLA-peptide affinity predictions determined by NetMHCpan version 4.0 algorithms. D) Predicted weak binding (rank 0.5–2%) neoantigens/patient partitioned into HLA-A, B, and C-specific peptides. E) BCRseq analysis as determined by the TRUST algorithm of tumor RNA-seq data from samples of TLS−, TLS+GC−, and TLS+GC+ patients. Shown is the calculated Simpsons clonality score for each patient. F) The rate of BCR somatic hypermutation is shown calculated by the number of unique mutated B cell clones per total unique B cell clones in each patient tumor. Statistical comparisons were made between all groups. If no p-value is displayed, the comparison was not statistically significant
