Figure 3.
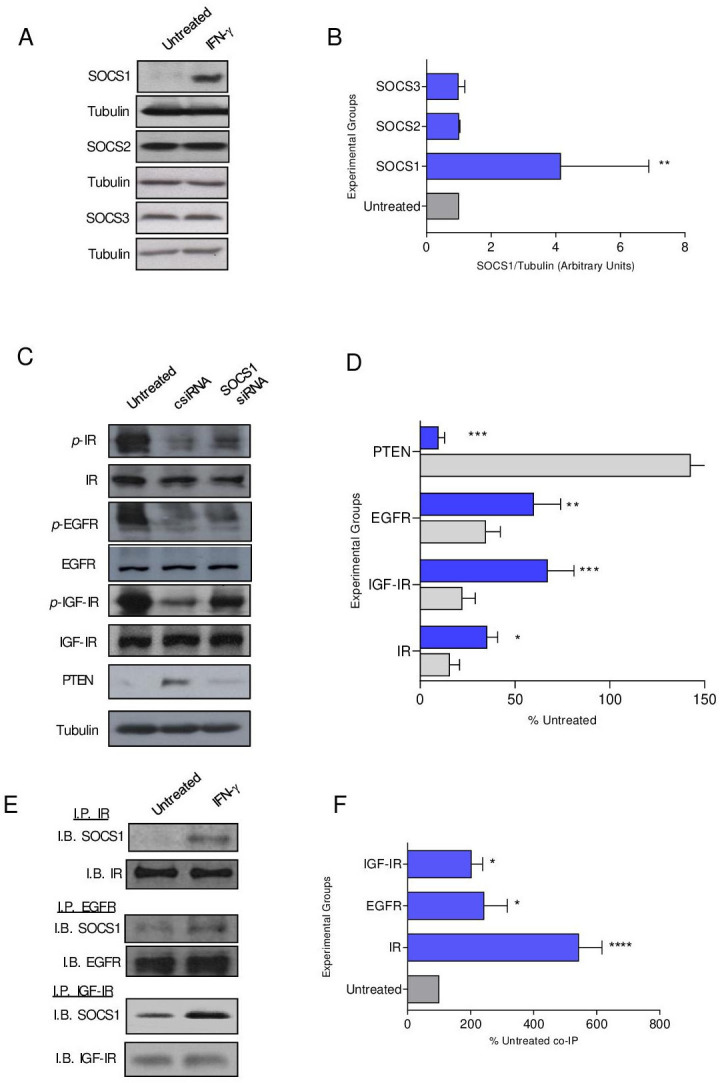
SOCS1 protein, induced by IFN-γ, directly binds to receptor tyrosine kinases to obstruct signaling. (A) Representative western blots and (B) densitometric quantification of the indicated SOCS protein expression after treatment with IFN-γ (blue bars) compared with the untreated control (gray bars) cells; n=3 independent experiments; **p<0.01. (C) Representative Western blots and (D) densitometric quantification of phospho-receptor tyrosine kinases in IFN-γ-treated cells after transfection with csiRNA (gray bars) or SOCS1 siRNA (blue bars) presented as a percent of the untreated (±SEM); n=3 independent experiments; **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. (E) Representative western blots and (F) densitometric quantification of the coimmunoprecipitation of SOCS1 with the indicated receptor tyrosine kinase after treatment with IFN-γ (blue bars) compared with the untreated (gray bar) cells presented as a percent of the untreated; n=3 independent experiments; ****p<0.0001, *p<0.05. csiRNA, control siRNA; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; IGF-IR, insulin-like growth factor receptor 1; p-IGF-IR, phosphorylated IGF-IR; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; p-EGFR, phosphorylated EGFR; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog;IB, immunoblot; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IP, immunoprecipitation; IR, insulin receptor; p-IR, phosphorylated IR; siRNA, small interfering RNA.
