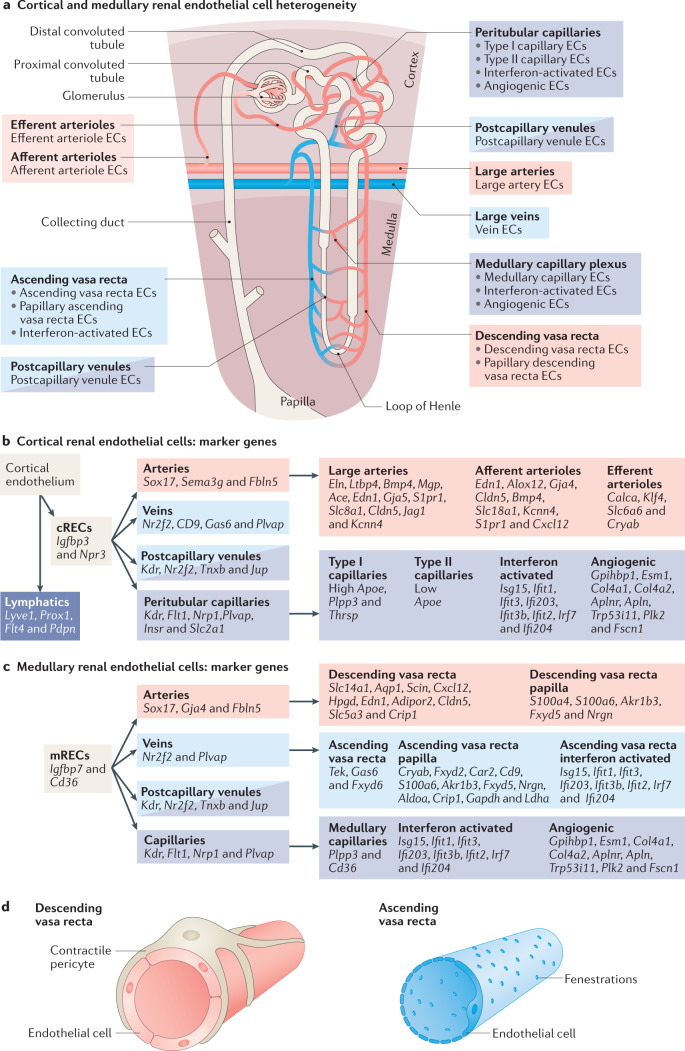
Fig. 3. Phenotypic and molecular heterogeneity of the cortical and medullary renal endothelium.
a | Phenotypically distinct renal endothelial cell (REC) phenotypes coexist within the two main anatomical compartments of the kidney, the cortex and medulla. b | Markers of different cortical REC (cREC) phenotypes. Since REC subpopulations express a combination of several markers, these are indicated following a hierarchical system. c | Markers of different medullary REC (mREC) populations. Since REC subpopulations express a combination of several markers, these are indicated following a hierarchical system. More detailed information regarding the expression and function of genes expressed in cortical and medullary RECs can be found in Supplementary Table 1. d | Phenotypic differences exist between the descending vasa recta (DVR) and the ascending vasa recta (AVR). The arterial-like ECs of the DVR are non-fenestrated and covered by a pericyte layer that regulates the medullary blood flow. By contrast, the venous-like ECs of the AVR are highly fenestrated and lack pericyte coverage, which facilitates water reuptake.