Figure 2:
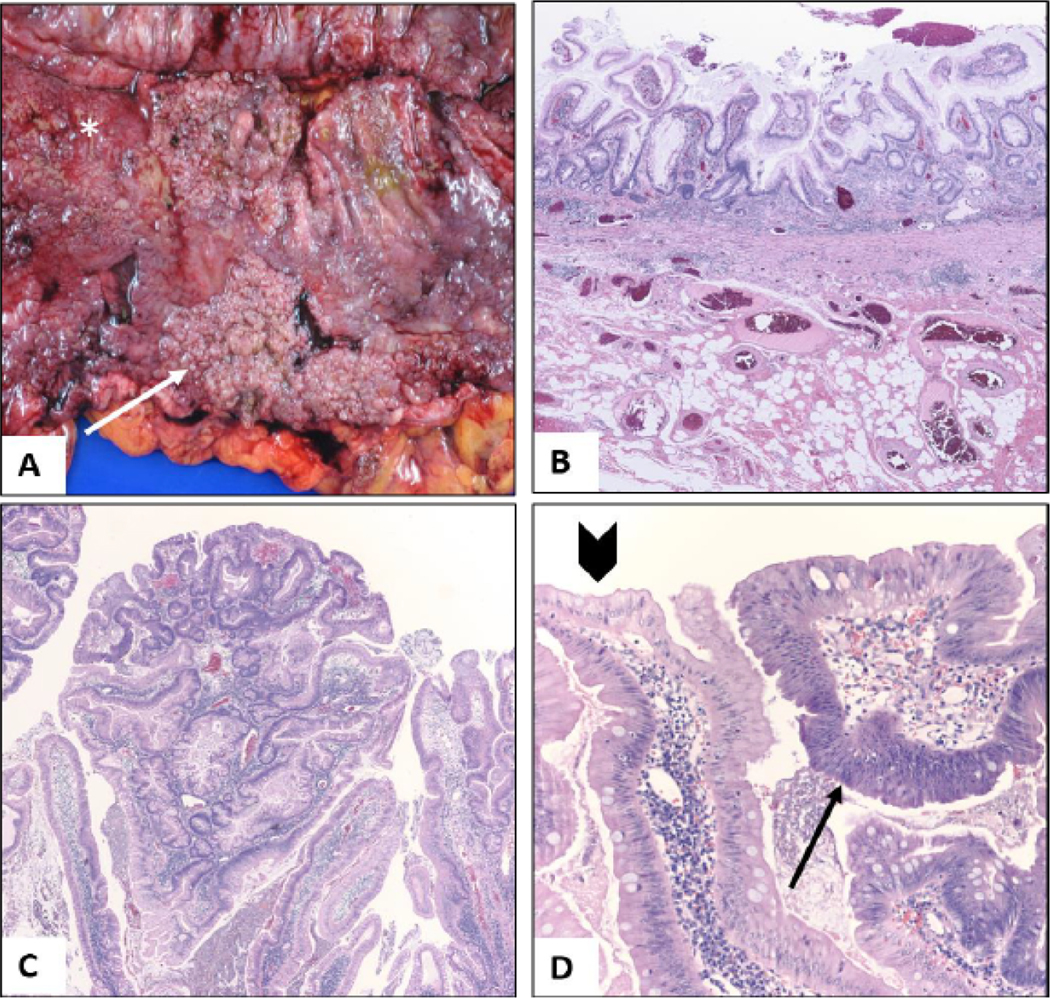
Pathology of colectomy specimen; (A) Gross appearance of sessile carpet-like polypoid lesion in the ascending colon (arrow) from the colectomy specimen. The adjacent mucosa is irregular and erythematous with loss of normal mucosal folds (asterisk); (B) On microscopy, the colonic mucosa was diffusely involved by chronic colitis, characterized by crypt distortion, basal plasmacytosis, and regenerative changes. The inflammation is limited to the mucosa (H and E, 4x); (C) Low power view of the ascending colon sessile lesion reveals proliferative mucosa forming polypoid structures (H and E, 4x); (D) On higher magnification, multiple areas of low-grade dysplasia (arrow) are seen. Compared to adjacent reactive epithelium (arrowhead) dysplastic foci show increased nuclear size, hyperchromasia, stratification and mucodepletion (H and E, 20X).
