Fig. 1. Uptake of recombinant wild type human aSyn and bSyn by OLN-93 cells.
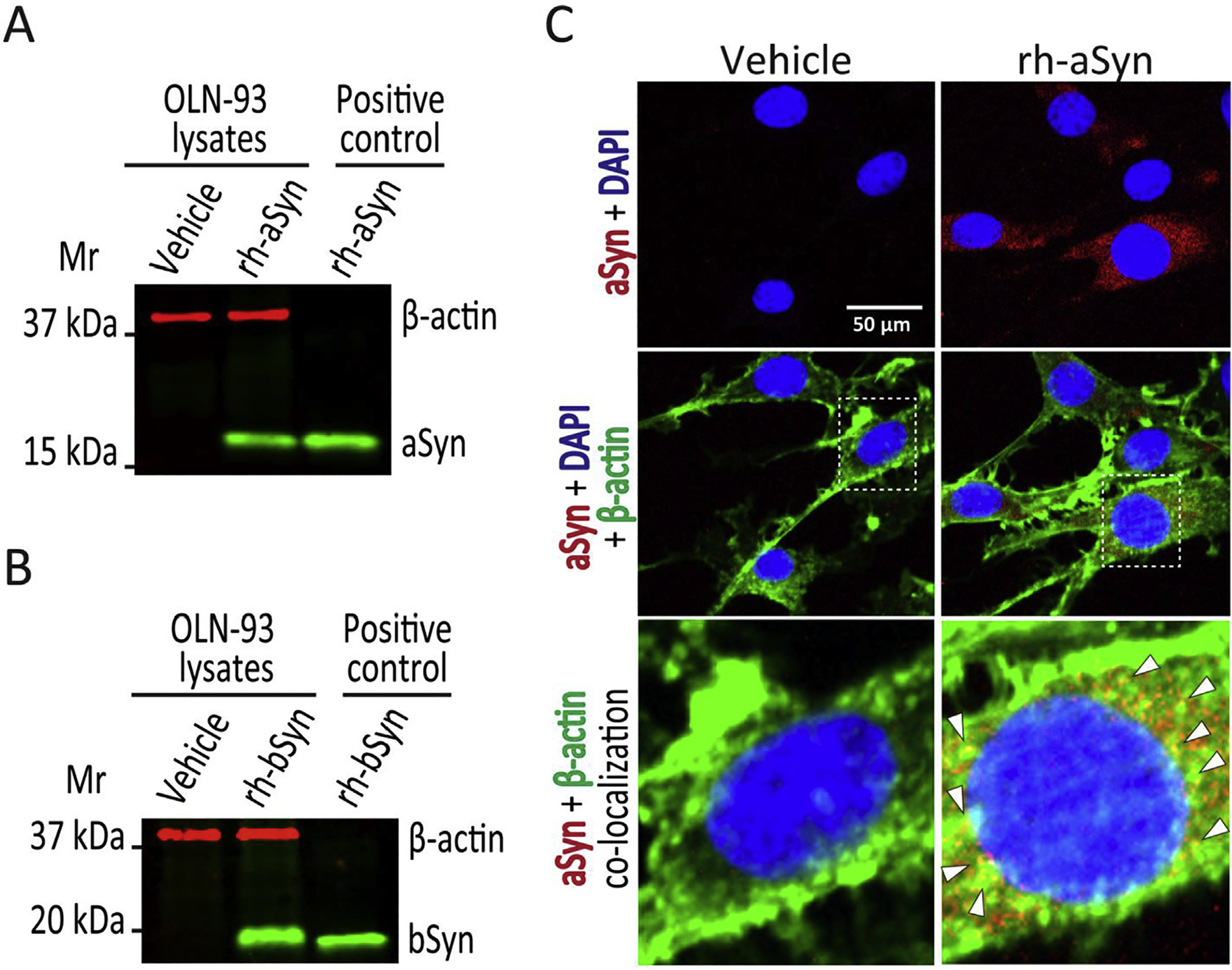
(A). Immunoblot of OLN-93 cell lysates after 12 h treatment with vehicle (lane 1) or 1 μM recombinant human wild type aSyn (rh-aSyn, lane 2), and recombinant human aSyn (25 ng) as positive control (lane 3). A 19 kDa aSyn band is apparent only in OLN-93 cells exposed to recombinant human aSyn and the positive control, with none noted for vehicle treated cells. (B). Immunoblot of OLN-93 cell lysates after 12 h treatment with vehicle (lane 1) or 1 μM recombinant human wild type bSyn (rh-bSyn, lane 2), and recombinant human bSyn (25 ng) as positive control (lane 3). A 20 kDa bSyn band is apparent only in OLN-93 cells exposed to recombinant human bSyn and the positive control, with none noted for vehicle treated cells. (C). Confocal microscopic images of OLN-93 cells treated with vehicle or 1 μM recombinant human aSyn for 12 h. Cells were stained for aSyn (Syn-1 antibody 1:100 dilution, red signal) and nuclei (DAPI, blue signal) (upper frames) show that aSyn is present only in OLN-93 cells treated with recombinant human aSyn (rh-aSyn, right frames). Merged images showing aSyn, DAPI plus β-actin (ActinGreen 488, green signal) (middle frames) show that aSyn signal is mainly confined to the cytosolic compartment. Enlarged images of nuclear and perinuclear area (lower frames) show co-localization of aSyn and β-actin (arrowheads pointing to yellow spots) mainly in the perinuclear area. Scale bar = 50 μm.
