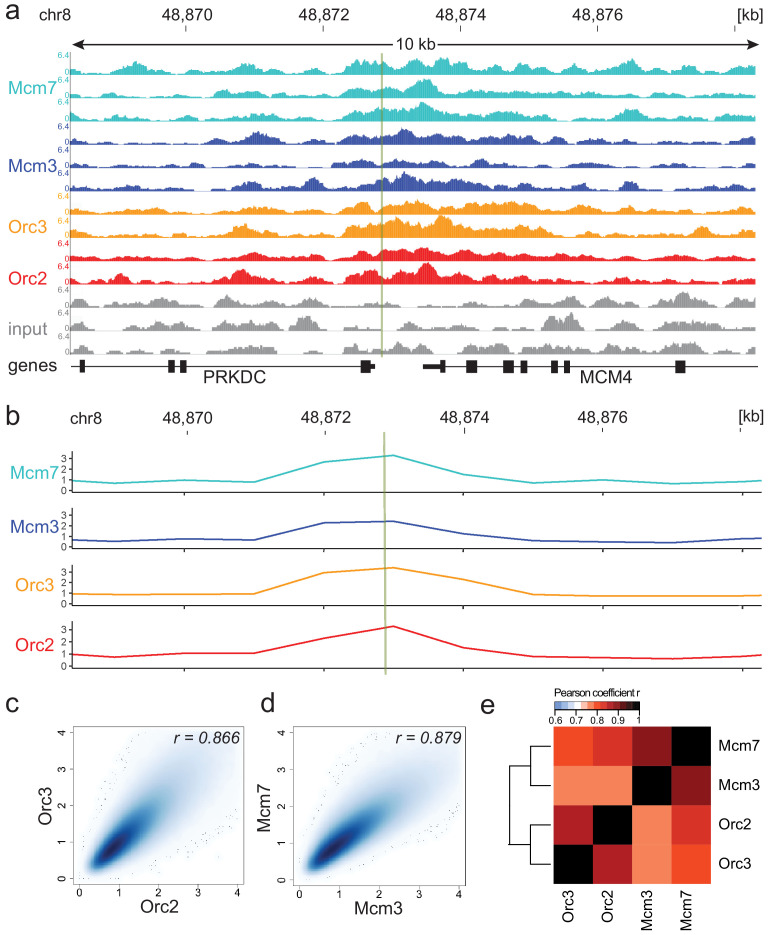
Figure 1. Moderate averaging represents a valid approach for origin recognition complex/minichromosome maintenance complex (ORC/MCM) chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) analysis.
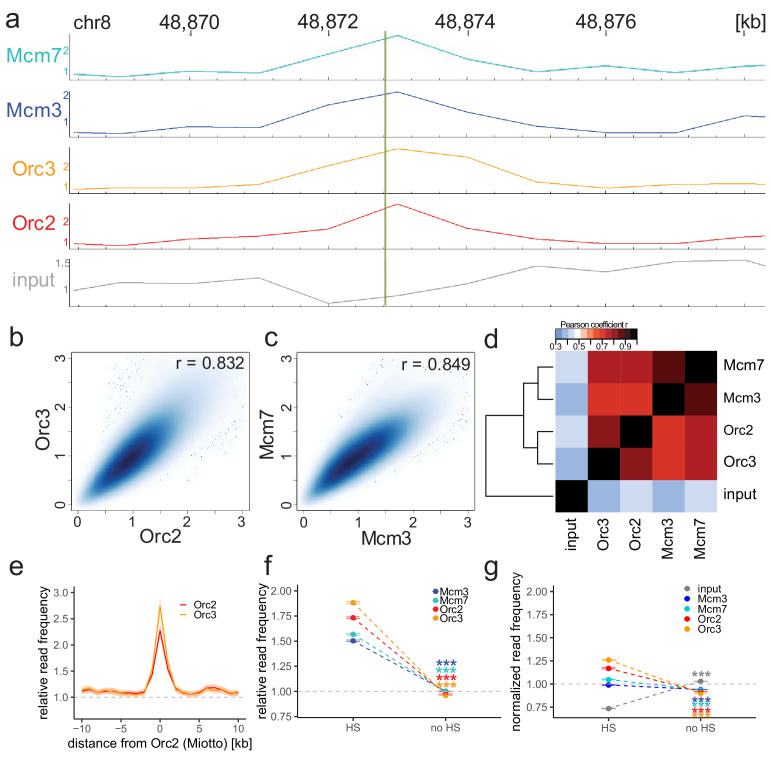
(a) Sequencing profile visualization in UCSC Genome Browser (hg19) at the Mcm4/PRKDC origin after reads per genomic content normalization: two samples of Orc2 and Orc3, and three samples of Mcm3 and Mcm7, are plotted against the input in three replicates. The profiles are shown in a 10 kb window (chr8: 48,868,314–48,878,313); the mapped position of the origin is indicated as green line. (b) The profile of ORC/MCM ChIP-seq after 1 kb binning at the same locus. The reads of replicates were summed and normalized by the total genome-wide ChIP read frequency followed by input division. Y-axis represents the resulting relative read frequency. (c) Correlation plot between Orc2 and Orc3 relative read frequencies in 1 kb bins. (d) Correlation plot between Mcm3 and Mcm7 relative read frequencies in 1 kb bins. (e) Heatmap of Pearson correlation coefficients r between all ChIP relative read frequencies in 1 kb bins. Column and line order were determined by complete linkage hierarchical clustering using the correlation distance (d = 1 r). Refer to Figure 1—figure supplement 3 for data representation without input division.