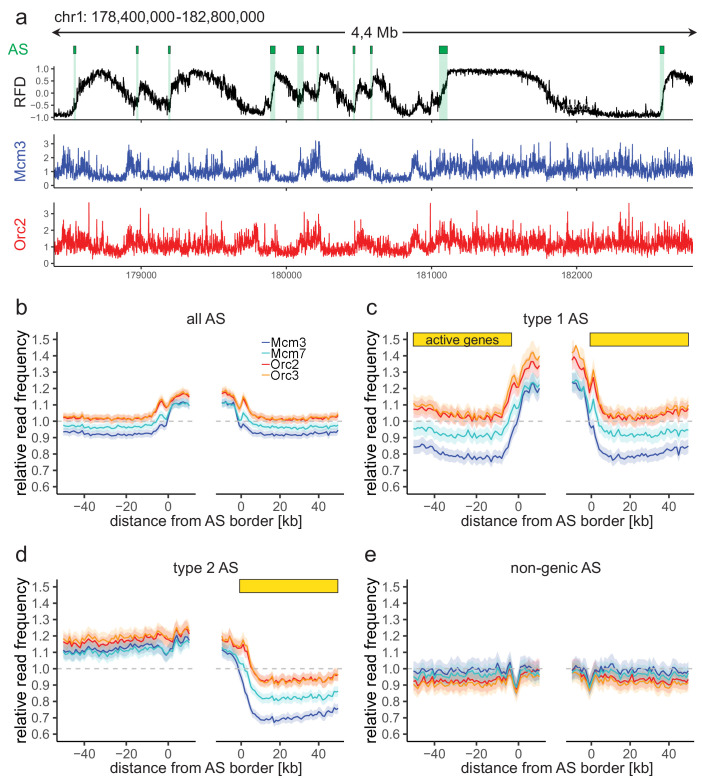
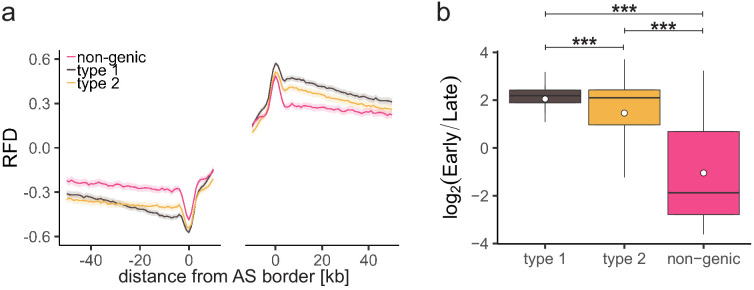
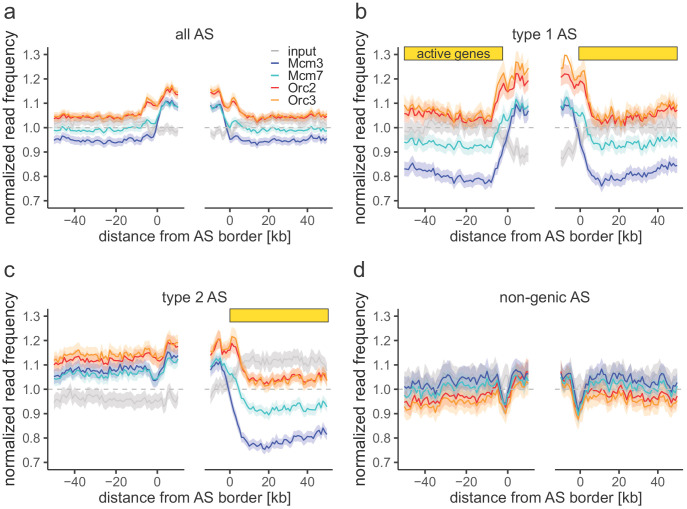
Figure 2. Origin recognition complex/minichromosome maintenance complex (ORC/MCM) enrichment within ascending segments (ASs) depends on active transcription.
(a) Top panel: example of an replication fork direction (RFD) profile on chr1: 178,400,000–182,800,000, covering 4 Mb. Detected ASs are labeled by green rectangles (irrespective of length and RFD shift). Middle and bottom panels: representative Mcm3 (blue) and Orc2 (red) chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) profiles after binning for the same region. (b–e) Average input-normalized relative ChIP read frequencies of Orc2, Orc3, Mcm3, and Mcm7 at AS borders of (b) all AS (L > 20 kb and ΔRFD >0.5; n = 2957), (c) type 1 ASs with transcribed genes at both AS borders (n = 673), (d) type 2 ASs oriented with their AS border associated to transcribed genes at the right (n = 1026), and (e) non-genic ASs in gene-deprived regions (n = 506). The mean of ORC and MCM relative read frequencies is shown ±2 × SEM (lighter shadows). The dashed grey horizontal line indicates relative read frequency 1.0 for reference. For type 1 and 2 ASs, yellow bars mark the AS borders associated to transcribed genes. Refer to Figure 2—figure supplement 2 for analysis without input division.