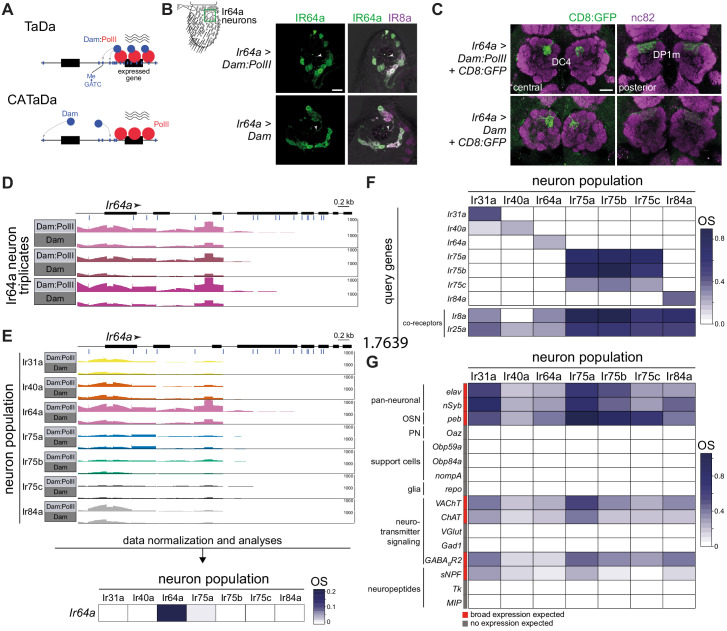
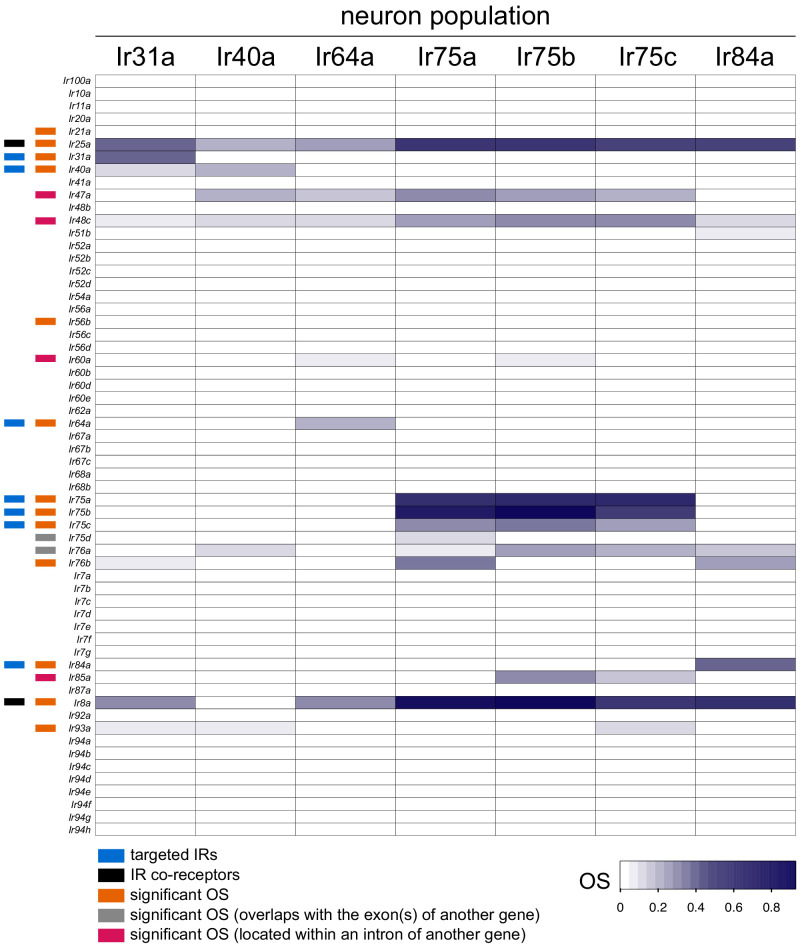
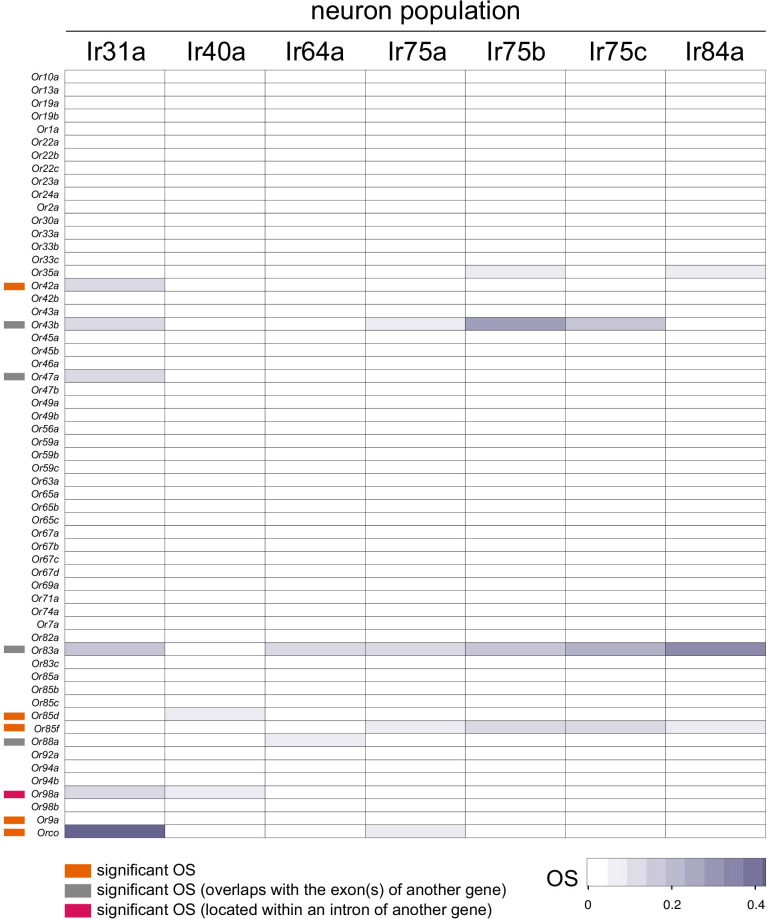
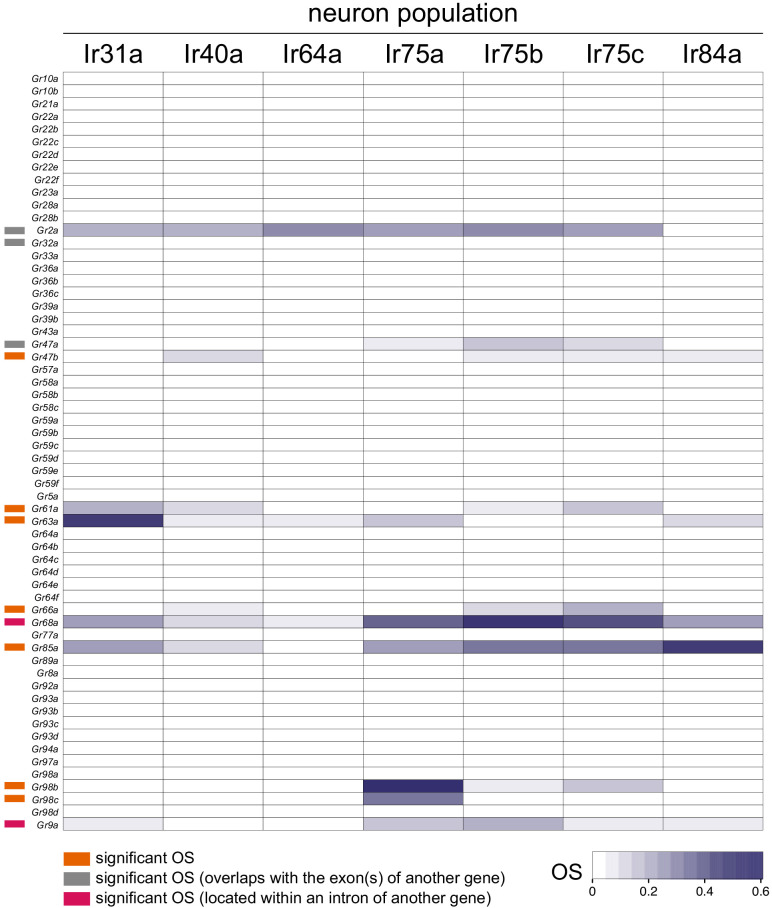
Figure 1. Targeted DamID of OSN populations.
(A) Schematic of the principles of Targeted DamID (TaDa) and Chromatin accessibility TaDa (CATaDa). TaDa reports on the enrichment of GATC methylation (Me; blue lines) by a Dam:PolII fusion (top) relative to Dam alone (bottom), thereby identifying PolII-transcribed genes. In CATaDa, analysis of methylation patterns of free Dam provides information on chromatin accessibility. (B) Immunofluorescence for IR64a and IR8a on antennal sections of animals expressing in Ir64a neurons either Dam:PolII (Ir64a-Gal4/+;UAS-LT3-Dam:RpII15/+) or Dam alone (Ir64a-Gal4/+;UAS-LT3-Dam/+). The approximate field of view shown is indicated by the green box on the antennal schematic on the left. The merged fluorescent channels are overlaid on a bright-field background to reveal anatomical landmarks. The arrowheads point to IR64a that is localized in the neuron sensory endings within the sensillar hairs. Scale bar = 10 µm. (C) Immunofluorescence for GFP and the neuropil marker nc82 on whole-mount brains of animals expressing in Ir64a neurons a CD8:GFP reporter together with Dam:PolII (Ir64a-Gal4/+;UAS-LT3-Dam:RpII15/UAS-mCD8:GFP) or free Dam (Ir64a-Gal4/+;UAS-LT3-Dam/UAS-mCD8:GFP). Two focal planes are shown to reveal the two glomeruli (DC4 and DP1m) innervated by Ir64a neurons. Background fluorescence in the GFP channel was slightly higher across the brain in the Dam-alone samples. Scale bar = 20 µm. (D) Illustration of raw sequence read data underlying the TaDa analyses. Bar heights indicate the read coverage of methylated GATC fragments mapping to the Ir64a gene (transcribed left-to-right, as indicated by the arrowhead; blue lines under the gene model indicate the position of GATC motifs). The precise transcription start site of Ir64a is unknown. For each of three replicate experiments, the top row is the Dam:PolII sample, which has higher read counts compared to the Dam-alone sample below. The y-axes (range 0–1000) indicate the read depth. (E) Top: comparisons among the seven Ir neuron datasets of the raw sequence reads mapping to the Ir64a gene for the Dam:PolII and Dam samples (a single representative replicate is shown for each). Genotypes are of the form shown in (B), except for Ir75a and Ir75c neuron populations where third chromosome Ir-Gal4 driver transgenes were used. Only the Ir64a population displays a higher read count for Dam:PolII samples compared to Dam-alone samples. The y-axes (range 0–1000) indicates the read depth. Bottom: heatmap representation of the occupancy scores (OSs) following data normalization and statistical analyses (based on data across the full gene body (see Materials and methods); color scale on the right) for Ir64a calculated across triplicates for each of the seven neuron populations. (F) OS heatmap for the seven target Ir genes, as well as the main Ir co-receptor genes, in the seven Ir neuron populations. OSs and FDR values associated with each Ir gene within the corresponding neuron population are shown in Supplementary file 5. (G) OS heatmap of diverse positive- and negative-control genes in the seven Ir neuron populations (i.e. with known or expected expression/lack of expression). Abbreviations are defined in the main text. See also Supplementary file 1 and DamID_files.zip (https://gitlab.com/roman.arguello/ir_tada/-/tree/main/DamID_analyses) for data.