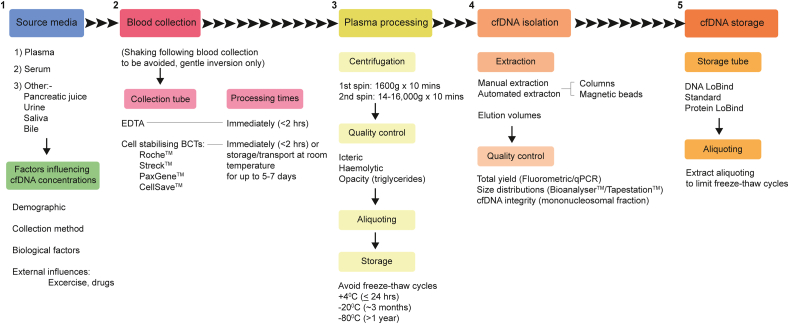
Fig. 3.
Guidelines for cfDNA isolation and analysis from peripheral blood. Recommended (1) preanalytical considerations and specific application requirements for (2) blood collection, (3) plasma processing, (4) cfDNA isolation and (5) cfDNA storage are shown. Best practice suggests that whole blood samples are processed as soon as possible following blood draw for plasma retrieval, particularly when collected in EDTA tubes. Cell stabilising collection tubes are also commercially available, that maintain sample integrity during transport, or when immediate in-house processing is not possible. During cfDNA extraction, the required concentration of input DNA for downstream applications should be considered when deciding on elution volumes (e.g. to provide the highest possible concentration of ctDNA fragments that are otherwise present at low concentrations in human plasma). Total extracted DNA yields can be measured using fluorometric or PCR-based approaches, and the quality of isolated DNA determined through the analysis of fragment size distributions. qPCR assays can also be used to make complementary assessments of cf-/ctDNA integrity and improve the stringency of sample validations for next-generation sequencing and digital PCR applications. Care should be taken when storing cfDNA samples to limit freeze thaw cycles, which can damage the integrity of fragmented cfDNA. BCT, blood collection tube.