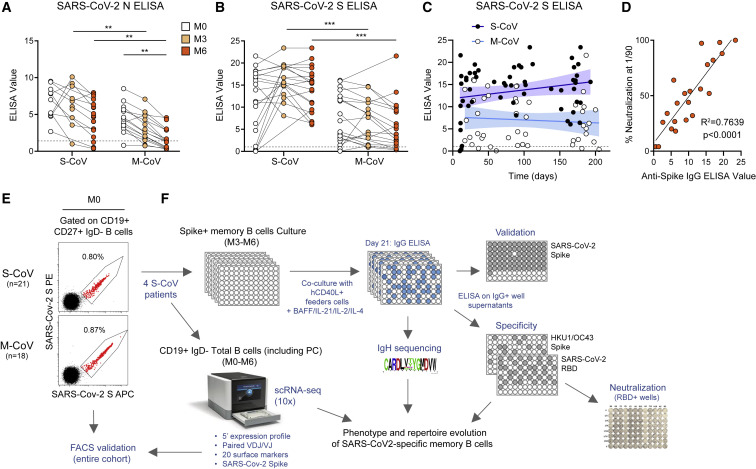
Figure 1.
Longitudinal characterization of the humoral response against SARS-CoV-2 in severe and mild COVID-19 patients
(A and B) Anti-SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) (A) and spike (S) (B) serum IgG levels were measured by ELISA in 21 severe COVID-19 (S-CoV) and 18 mild COVID-19 (M-CoV) patients at M0 (white), M3 (light orange), and M6 (dark orange). The dashed line indicates the positivity threshold provided by the manufacturer.
(C) Evolution of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S serum IgG levels over time post symptom onset in S-CoV (black dots, dark blue line) and M-CoV (white dots, light blue line) patients. Continuous lines indicate linear regression, and colored area between dashed lines indicates error bands (R2 = 0.049 for S-CoV, ns and 0.0061 for M-CoV, ns, Pearson correlation).
(D) Correlation between anti-SARS-CoV-2 S serum IgG levels and in vitro neutralization potential (% neutralization achieved at a 1/90 dilution) at M6 (n = 10 S-CoV and 11 M-CoV patients). The line represents a simple linear regression (R2 and p value with Pearson correlation are shown)
(E) Representative FACS plot of His-tagged SARS-CoV-2 S staining in gated live CD19+CD38int/−CD27+IgD− B cells at M0 in two representative S-CoV (upper plot) and M-CoV patients (lower plot).
(F) Overall study design.
ANOVA and two-tailed Mann-Whitney tests (A and B). Linear regression with Pearson correlation analysis (D). ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗p < 0.01. See also Figure S1 and Table S1.