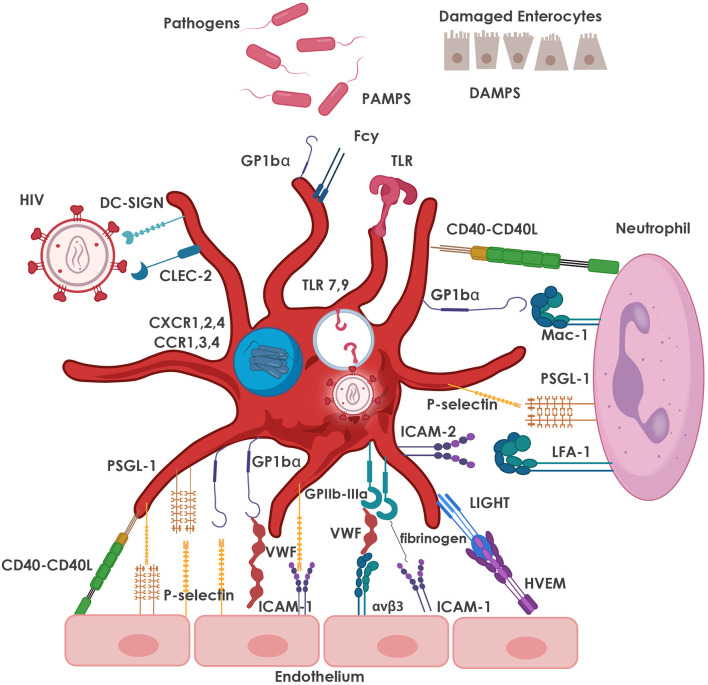
Figure 2.
Major adhesive interactions between platelets and pathogens, including HIV, as well as with neutrophils and the endothelium. Platelets express TLRs which are activated by PAMPs and DAMPs, resulting in the release of immune mediators that facilitate pathogen clearance. Platelets also express DC-SIGN and CLEC-2 which facilitate the interaction of platelets with HIV-1. Internalized virus interacts with endosomal TLR7, as well as TLR9, leading to increased platelet activation. Platelet granules also express CXCR1, 2, 4 and CCR1, 3, 4 co-receptors that are also used for interaction with HIV-1. Neutrophil-platelet interaction is primarily mediated by the binding of CD62P on platelets to its counter-receptor, PSGL-1, on the neutrophil surface, and platelet glycoprotein (GP) Ibα binding to neutrophil Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). Other major pro-adhesive interactions between platelets and neutrophils involve CD40 and ICAM-2 on the platelet with CD40L and LFA-1 on the neutrophil. The most relevant interactions between platelets and endothelial cells are depicted, namely platelet GPIbα (in the GPIb-IX-V receptor complex) with von Willebrand factor (VWF) released from the endothelium; bi-directional binding of CD62P with PSGL-1 or GP1bα; platelet GPIIb/IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) with endothelial αvβ3 (via VWF, fibrinogen, fibronectin), ICAM-1 (via fibrinogen); and GPIb-IX-V (via VWF). Various markers of platelet activation have been found to be upregulated in HIV-infection and include CD62P, CD40L and LIGHT (TNFSF 14). CCR, C-C chemokine receptor; CD40L; CD40 ligand; CD62P, P-selectin; CLEC-2, C-type lectin receptor 2; CXCR, C-X-C chemokine receptor; DAMPs, damage-associated molecular patterns; DC-SIGN, dendritic cell-specific soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1-3-grabbing non-integrin; GP, glycoprotein; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule; LFA, leukocyte function associated antigen; Mac-1, macrophage-1 antigen; PAMPs, pathogen-associated molecular patterns; PSGL-1, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand; TLR, Toll-like receptors; TNFSF, tumor necrosis factor superfamily; VWF, von Willebrand factor.