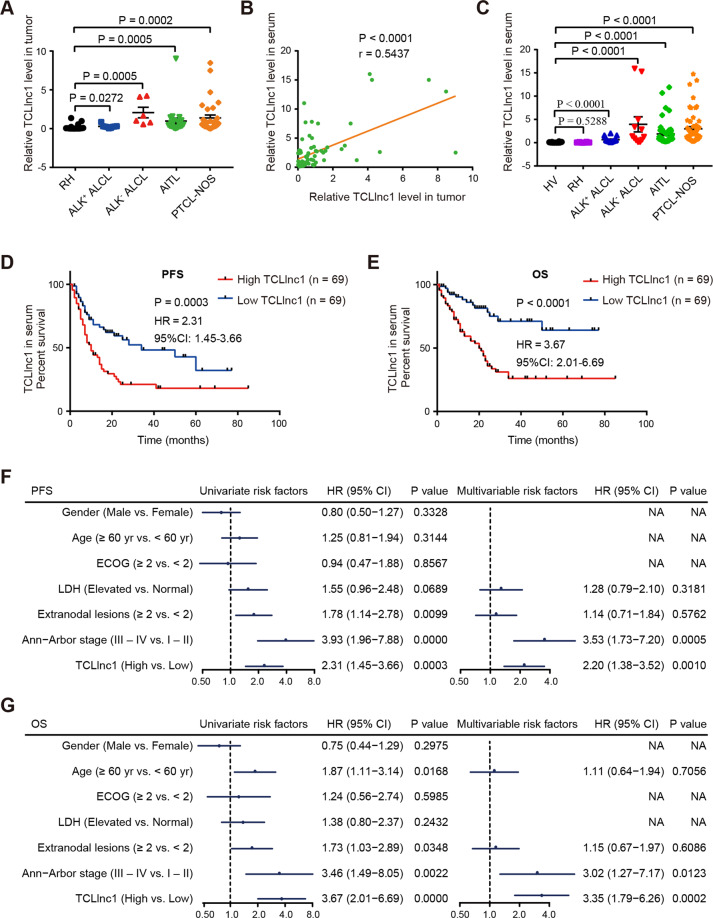
Fig. 2. TCLlnc1 was clinically relevant in PTCL.
A Expression of TCLlnc1 in tumors of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL)-anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive (ALK+ALCL, n = 9), ALCL-ALK negative (ALK−ALCL, n = 6), angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL, n = 23), and peripheral T cell lymphoma-not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS, n = 32), as compared to RH (n = 16) by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). B Correlation between TCLlnc1 expression in tumor and in serum of PTCL patients (n = 70). C Expression of TCLlnc1 in serum of RH (n = 10), ALK+ALCL (n = 18), ALK−ALCL (n = 12), AITL (n = 53), and PTCL-NOS (n = 55) in comparison with healthy volunteers (HV, n = 10). TCLlnc1 expression was quantified by qRT-PCR. D, E Progression-free survival (PFS, D) and overall survival (OS, E) of PTCL patients according to TCLlnc1 expression in serum (n = 138). F, G Univariate and multivariate analysis for PFS (F) and OS (G) in PTCL (n = 138).