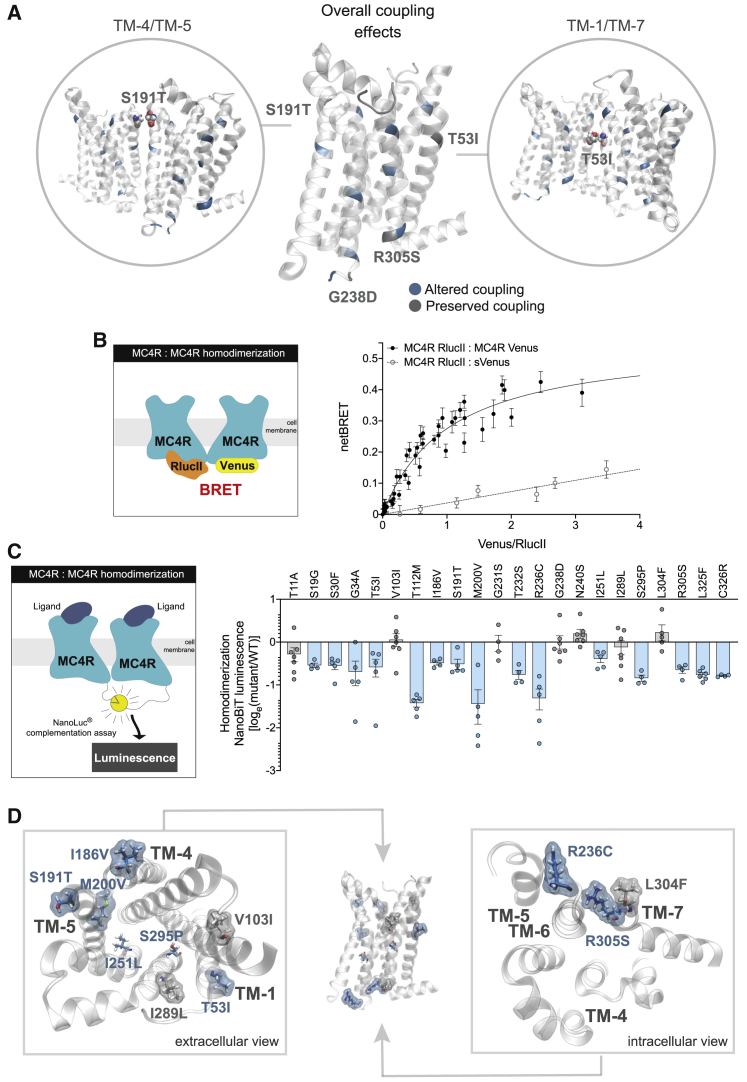
Figure 5.
Structural mapping of MC4R mutants suggests impaired dimerization
(A) Receptor mutants affecting at least one coupling partner (blue) and those that do not affect coupling (gray). Two of the latter map to one of the proposed MC4R homodimeric interfaces, being within 4Å of the opposite MC4R partner (shown in gray in a van der Waals representation). S191T maps to a TM-4/TM-5 interface (left inset); T53I maps to a TM-1 /TM-7 interface (right inset).
(B) BRET saturation curve from HEK293SL cells co-transfected with a constant amount of MC4R RlucII donor construct and increasing amounts of the MC4R Venus acceptor construct. Soluble (s) Venus acceptor construct was used as a negative control.
(C) MC4R WT:MC4R mutant receptor dimerization as measured in NanoBiT protein:protein interaction assay (see STAR Methods). Data are expressed as loge (mutant/WT) and plotted as mean ± standard error from 4–7 independent experiments. Mutants were classified as LoF (blue) or WT-like (gray) based on statistically significant differences between WT and mutant (unpaired t test with Welch’s correction; p < 0.05).
(D) Structural mapping of variants affecting dimerization (blue sticks) and variants with preserved dimerization (gray sticks). Membrane-facing residues are highlighted in a surface representation. The left panel shows details from a top (extracellular) view of the receptor, whereas the right panel shows a bottom (intracellular) view.
See also Figure S4.