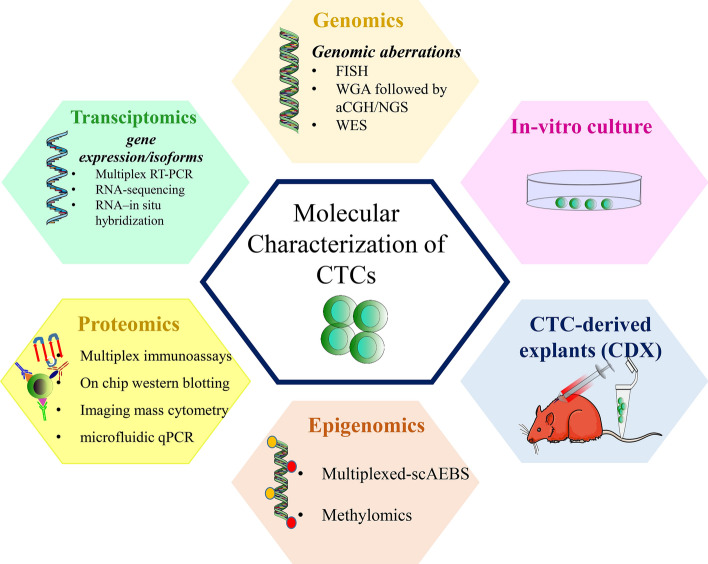
Fig. 4.
Molecular Characterization of CTCs. Various molecular features of CTCs can be characterized by using various recent technologies. CTC genomics can be studied by detecting various genomic aberrations using assays like FISH, WGA followed by aCGH/NGS and WES. CTC gene expression, as well as CTC-specific isoforms, can be demonstrated using technologies like multiplex RT-PCR, RNA-sequencing and RNA–in situ hybridization. The proteome of CTCs can be explored using recent advanced techniques such as multiplex immunoassays, on-chip western blotting, imaging mass cytometry and microfluidic qPCR. CTC-specific epigenomes can be studied using techniques like multiplexed-scAEBS and methylomics. Functional properties of CTCs such as their potential to form overt metastases could be explored by developing CDX models. In vitro, CTC cultures might be used for drug screening, personalized treatment and can provide insights into new pathways specific to metastasis-initiator CTCs and thus new therapeutic targets. FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridizations; WGA: Whole genome amplification CGH; Array competitive genome hybridization; NGS: Next generation sequencing; WES: Whole exome sequencing; scAEBS: single-cell- agarose-embedded bisulfite sequencing; CDX- CTC-derived explants