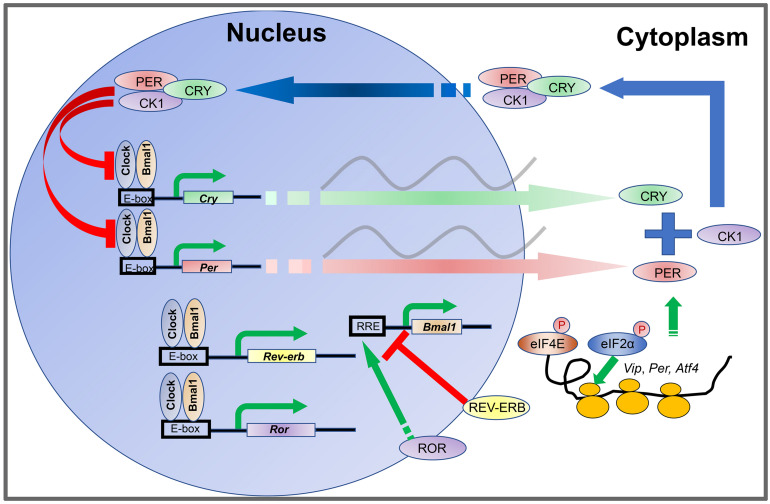
FIGURE 1.
Transcription-translation feedback loops (TTFLs) in the mammalian circadian clock. The CLOCK and BMAL1 proteins are activators and form a heterodimer to bind to E-box enhancers in the promoters of Per and Cry genes. PER and CRY proteins are synthesized during the day and form a protein complex which accumulates in the cytoplasm during the afternoon and evening. Upon reaching certain level, the PER-CRY complexes translocate into the cell nucleus during the nighttime and block the activities of the CLOCK: BMAL1 heterodimer to inhibit their own gene transcription. In addition, the CLOCK: BMAL1 complex also promotes the transcription of Rev-erb and Ror. REV-ERB in turn inhibits Bmal1 transcription whereas ROR promotes Bmal1 transcription. The abundance of PER proteins is controlled at the level of mRNA translation by rhythmic phosphorylation of eIF4E. Phosphorylation of eIF2α promotes translation of Atf4. ATF4 directly activates Per2 transcription. At the posttranslational level, levels of PER and CRY protein are regulated by phosphorylation and ubiquitination-mediated protein degradation CKI phosphorylates PER. Phosphorylation of PER and CRY proteins promotes their degradation and speeds up the clock.