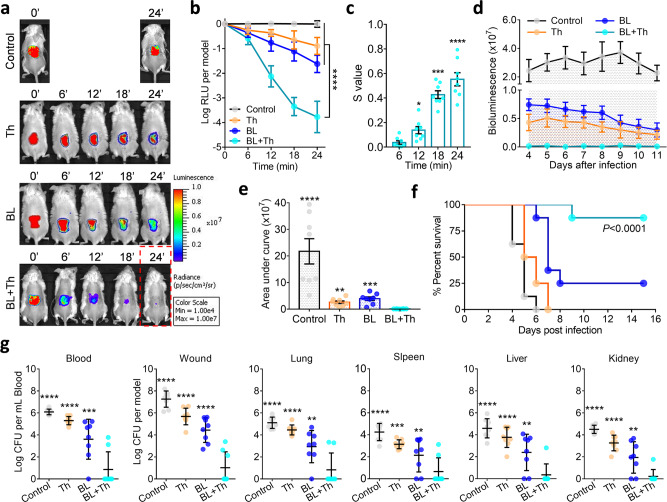
Fig. 4. BL together with thymol rescues mice from lethal USA300 biofilm-associated infection.
Murine 3rd-burn-wounds were infected with USA300 at 5 × 107 CFU in 50 µL of PBS for 72 h to form mature biofilms. The infected wounds were treated with sham (control), 50 µL of thymol at 10 mg/mL (Th), indicated times of BL (BL), or both (BL + Th). a Bacterial luminescence images of representative wounds were acquired at indicated times. b Mean luminescence was acquired over time and presented as log RLU per model. c, S-values are calculated by the Bliss Independence model as Fig. 2. d and e Mean luminescence was acquired from days 4 to 11 after an indicated treatment and the mean areas under the luminescence curves were summarized in e. f Kaplan–Meier survival curves of USA300 biofilm-associated mice in response to an indicated treatment. g Bacterial loads in the blood, wounds, lungs, spleens, livers, and kidneys were quantified just prior death or on day 15 after bacterial inoculation. All results are presented as mean ± SD of eight biological replicates. Zero in g was below the detection limit (40 CFU per model for murine wounds or organs and 20 CFU per mL blood). ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; and ns, no significance.