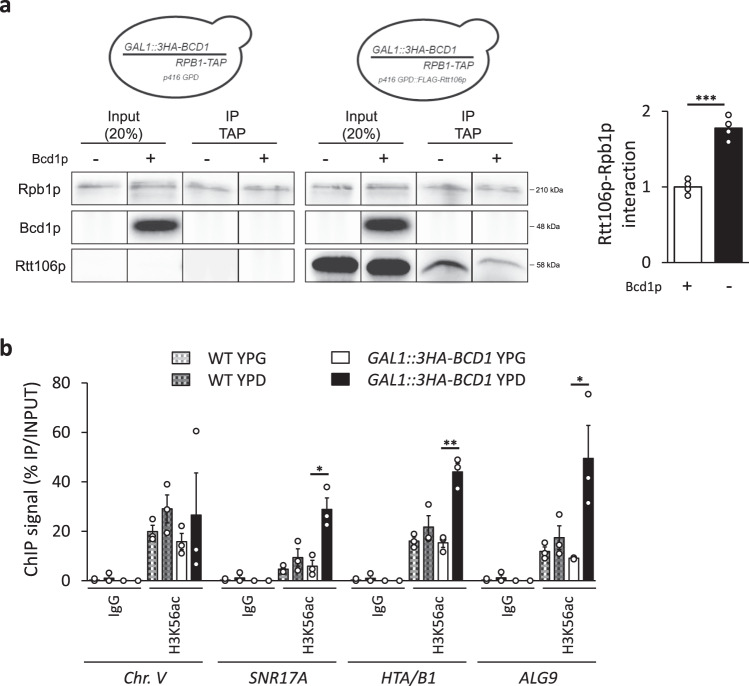
Fig. 4. Bcd1p controls transcription-dependent activity of Rtt106p.
a Interaction of Bcd1p with the RNA polymerase II large subunit Rpb1p in yeast. Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) was performed on GAL1::3HA-BCD1 × RPB1-TAP cells transformed with p416GDP::FLAG-Rtt106p expressing 3xHA-tagged Bcd1p, TAP-tagged Rpb1p and FLAG-Rtt106p. Cells were transformed with empty vector p416GDP as a control. Cells were grown in YPG (+Bcd1p) or YPD (−Bcd1p). Procedure was as described in Fig. 2b but with the IP performed with anti-TAP antibodies. The image corresponds to a cropping of different sections of the same membrane. The full-length membrane incubated with different antibodies is presented in the Source data file. Histogram on the right presents quantification of Western blots obtained from six independent co-IP experiments. Quantification was performed using Fusion Solo (Vilber Lourmat) and Fusion-Capt Advance Solo 4 software. The FLAG signal (Rtt106p) was normalized to the TAP signal (Rpb1p). The data represent mean values plus standard error to the mean of four biological replicates. b Depletion of Bcd1p affects H3K56ac levels at several RNA polymerase II-dependent genes. ChIP H3K56ac enrichment (IP/INPUT) for parental BY4741 strain and the GAL1::3HA-BCD1 strain grown in YPG (+Bcd1p) or YPD (−Bcd1p) is presented. Signal specificity was controlled with IgG antibodies. The histogram represents mean values plus standard error to the mean of three biological replicates. Two-tailed t-tests: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. In panel a, *** = 0.0001; in panel b, * = 0.011 for SNR17A (U3), ** = 0.002 for HTA/B1, * = 0.039 for ALG9. Source data for these panels are provided as Source Data files.