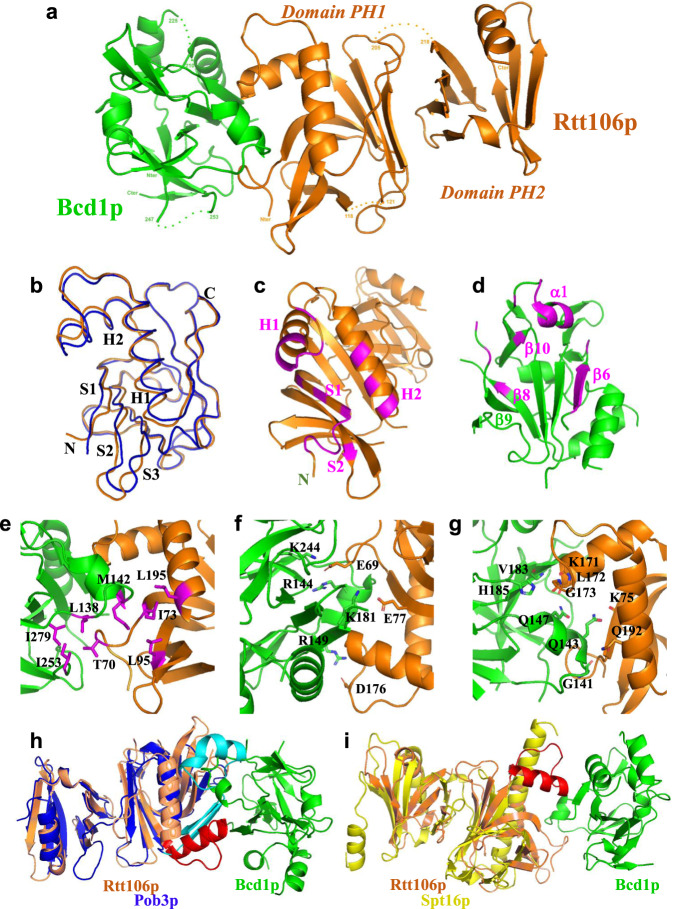
Fig. 6. Bcd1p120-303 interacts with the PH1 domain of Rtt106p65-301.
a Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the complex between Rtt106p65-301 and Bcd1p120-303. Rtt106p is in orange and Bcd1p in green. b Superimposition of the PH1 domain of Rtt106p bound to Bcd1p (in orange) and in a free state (in blue, entry PDB code 3TW122 [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3TW1]). H = Helix, S = Strand, N = N-terminal extremity, C = C-terminal extremity. c Residues located at the molecular surface of Rtt106p that are buried upon Bcd1p binding are in magenta. d Residues located at the molecular surface of Bcd1p that are buried in the Rtt106p:Bcd1p interface are in magenta. e–g Hydrophobic contacts, salt-bridges, and hydrogen bonds at the Rtt106p:Bcd1p interface: e Hydrophobic cluster (magenta) at the interface of the heterodimer. f Charged residues located at the interface form ionic interactions between Rtt106p and Bcd1p. g Network of hydrogen bonds between Rtt106p and Bcd1p. h, i Comparison of the 3D structures of Pop3p (in blue, entry PDB code 4PQ0 [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4PQ0]) and Spt16p (in yellow, entry PDB code 4IOY [https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4IOY]). The sequence spanning amino acids 162–182 in Rtt106p, which differs strongly from Pob3p and Spt16p, is in red.