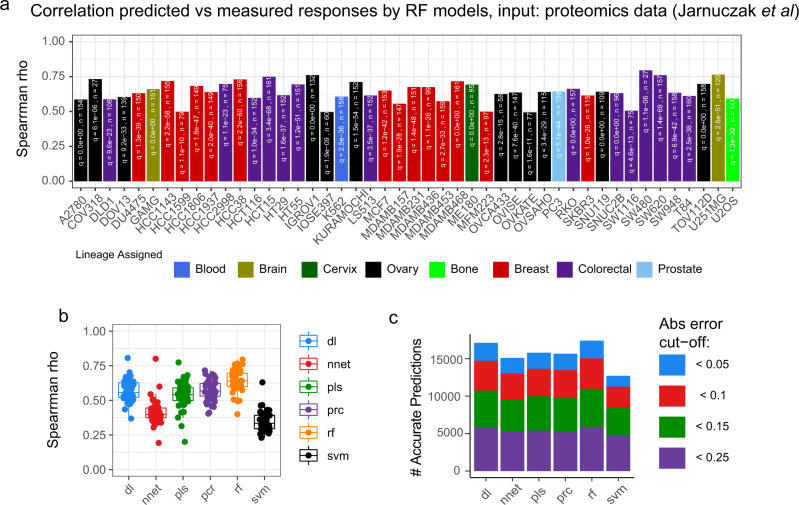
Fig. 6. Accuracy assessment of DRUML to rank drugs based on efficacy using independent proteomics datasets derived from 47 tumor models and 8 pathologies.
DRUML was used to predict drug responses for 47 cell lines using proteomic data obtained from 12 different laboratories and compiled by Jarnuczak et al. (Vizcaino lab, PRIDE PXD013455). Statistical significance of predictions was measured using Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient and Rho values are shown in figures (a and b). a Comparison of measured vs predicted drug responses within cellular models using the random forest method. Samples are colored by sample origin. b Distribution of Spearman rho correlation values between predicted and actual drug responses for all samples separated by ML learning algorithm. This boxplot has median centers, interquartile box boundaries and range upper and lower hinges. c Comparisons of the proportion of accurate predictions at 0.05, 0.1, 0.15 and 0.25 error cut-offs returned by the different ML methods. Learning algorithms were random forest (rf), cubist, bayesian estimation of generalized linear models (bglm), partial least squares (pls), principal component regression (pcr), support vector machine (svm), deep learning (dl) and neural network (nnet).