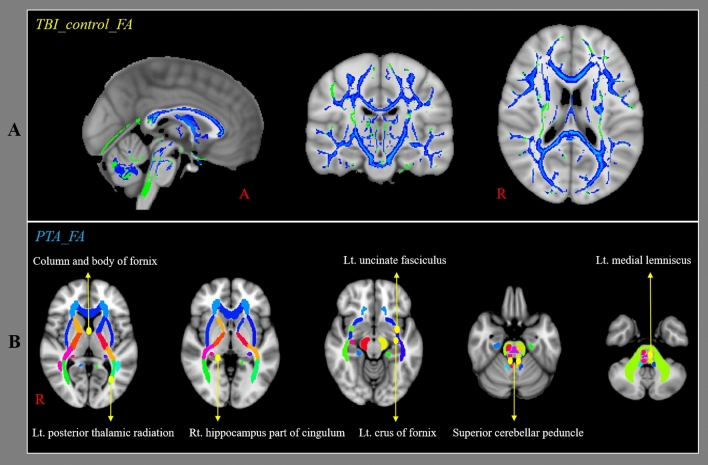
Figure 1.
Results of tract-based spatial statistics analyses comparing the fraction anisotropy (FA) values of the patients and control groups and the correlation between post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) duration and FA values of patients. FA values were obtained for 48 regions of interest (ROIs) using a standard template of the John Hopkins University diffusion tensor imaging-based white matter atlases within the Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Brain Software Library (FSL version 5.1; www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl). (a) The blue voxels indicate areas with higher mean FA values in the control group than in the patient group. (b) Among the 48 ROIs, the FA values of eight ROIs (column and body of fornix, left crus of fornix, left uncinate fasciculus, right hippocampus part of cingulum, left medial lemniscus, right superior cerebellar peduncle, left superior cerebellar peduncle, left posterior thalamic radiation including optic radiation) in the patient group were negatively correlated with PTA.