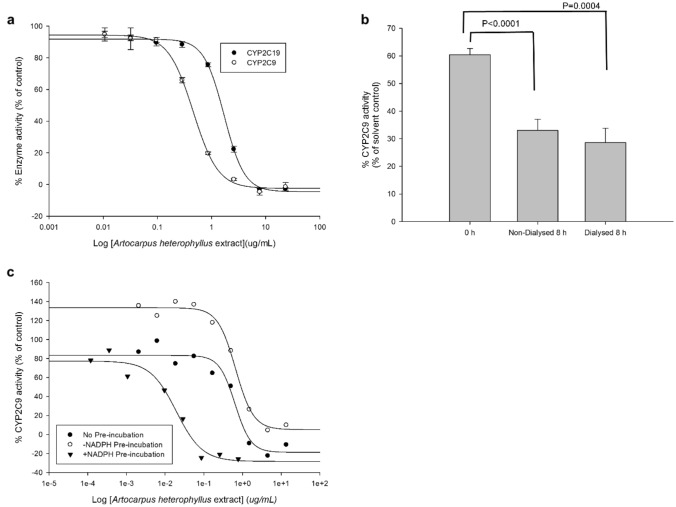
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effects of the A. heterophyllus extract on human CYP2C9-mediated 7-methoxy-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin demethylase (80 µM) and CYP2C19-catalyzed 3-cyano-7-ethoxycoumarin deethylase (25 µM) in vitro activities. (a) A. heterophyllus extract concentration-dependent inhibition of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 activities. Control activities performed with methanol (mean ± SEM) for CYP2C9 and 2C19 were 5.84 × 10−4 ± 3.56 × 10−5 and 8.01 × 10−3 ± 2.83 × 10−4 µM metabolite formed per min/pmol of CYP, respectively. (b) Effect of dialysis on the inactivation of human recombinant CYP2C9 activity by the A. heterophyllus extract. For (a) and (b), each data point is the mean percentage of control enzyme activity for three independent experiments. A p value ≤ 0.05 was considered statistically significant. (c) Effect of preincubation in the presence or absence of NADPH on the inhibition of human recombinant CYP2C9 activity by the A. heterophyllus extract.