FIGURE 2.
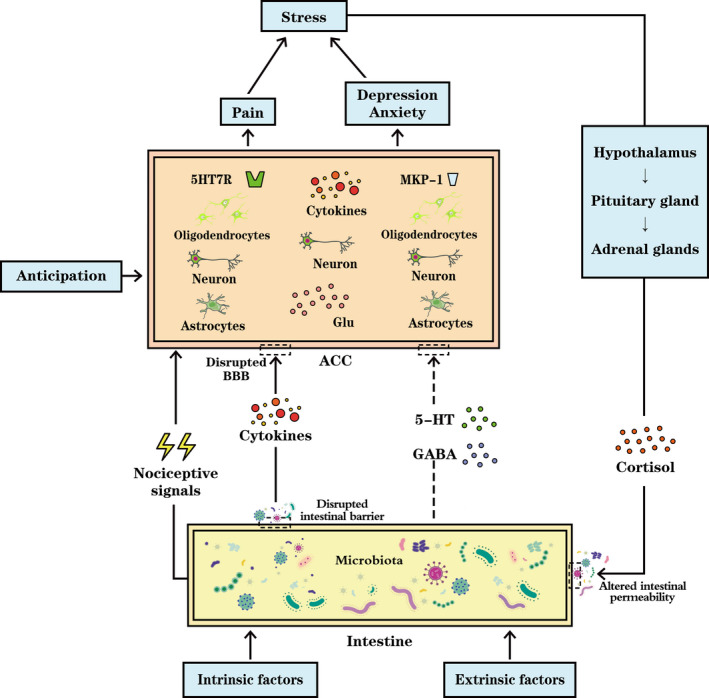
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) undergoes long‐term potentiation by processing nociceptive signals, and excessive glutamate (Glu) release may lead to neuronal injury. Overexpression of mitogen‐activated kinase phosphatase‐1 (MKP‐1) in the ACC has been implicated to trigger depression. The uncertainty and anticipation in patients with CD may induce anxiety and lead to ACC activation. Symptoms aggravate stress, activating the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis, secreting cortisol, and increasing intestinal permeability. Gut microbiota, the composition of which is influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors, regulate intestinal barrier function. In case of dysbiosis, bacteria and their products can cross the barrier, eliciting inflammatory cytokine release and increasing blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Circulating cytokines cross the BBB, inducing astrocyte and oligodendrocyte apoptosis, further disrupting BBB integrity. It is still to be ascertained whether gamma‐aminobutyric acid (GABA) and 5‐HT generated by microbiota can cross the disrupted BBB of patients with CD, for 5HT7R has a marked impact on brain remodeling
