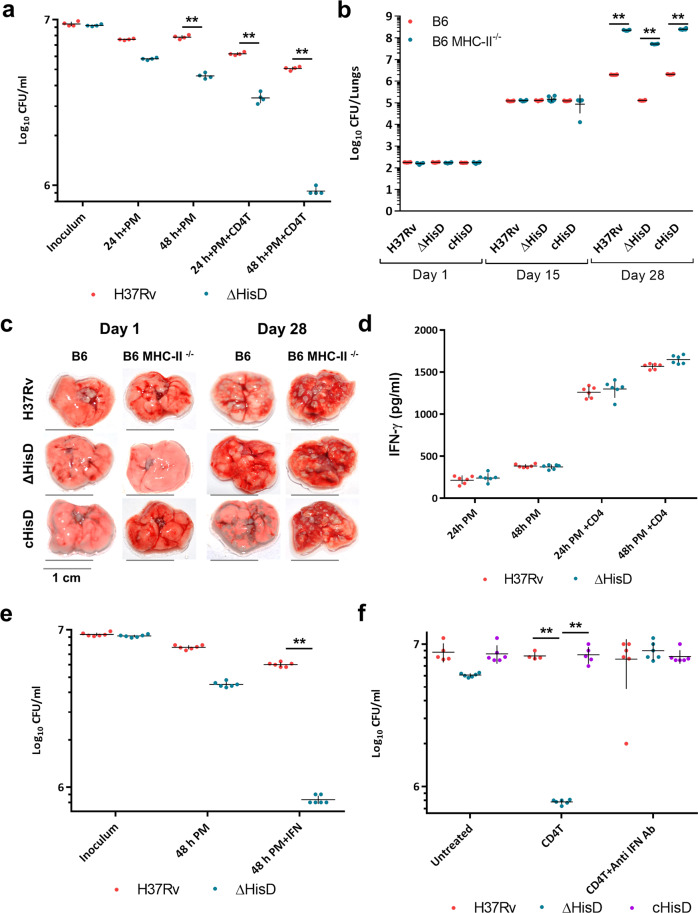
Fig. 4. A CD4 directed IFN-γ mediated bacillary clearance of Mtb histidine auxotroph.
a Bacillary counts for ΔhisD are decreased by 10-fold compared to H37Rv at 48 h post-infection, suggesting a possible role of CD4 T-cell-based activation of macrophages in the enhanced clearance of ΔhisD (n = 3 independently acquired and cultured primary cells; mean and SEM; **P-value < 0.005). b The bacillary counts for H37Rv and chisD each sharply rise as high as 108 and for ΔhisD as 107.5 on day 28 post infection in infected B6 MHC-II−/− mice lungs. (n = 6 individual mice per time point; mean and SEM; **P-value < 0.005). c A high degree of lung damage in the external pathophysiology is observed 28 days post infection with H37Rv, ΔhisD and chisD in B6 MHC-II−/− null mice (pictures are representative of three individual mice lungs samples). d While un-stimulated macrophages show low titres of secreted IFN-γ, CD4 T cell activated macrophages show high levels of IFN-γ (1600 pg ml−1) in culture medium 48 h post infection (n = 6 measurements from independently acquired and cultured primary cells; mean & SEM). e External supplementation of IFN-γ (~3000 pg ml−1) post infection onto infected primary macrophages led to equivalent decrease in bacterial counts of ΔhisD as in case of CD4 T cell activated macrophages (n = 6 independently acquired and cultured primary cells; mean and SEM, **P-value < 0.005). f Abrogation of the bactericidal activity post treatment with anti-IFN antibodies observed in CD4 T cell stimulated macrophages infected with ΔhisD (n = 6 independently acquired and cultured primary cells; mean and SEM; **P-value < 0.005).