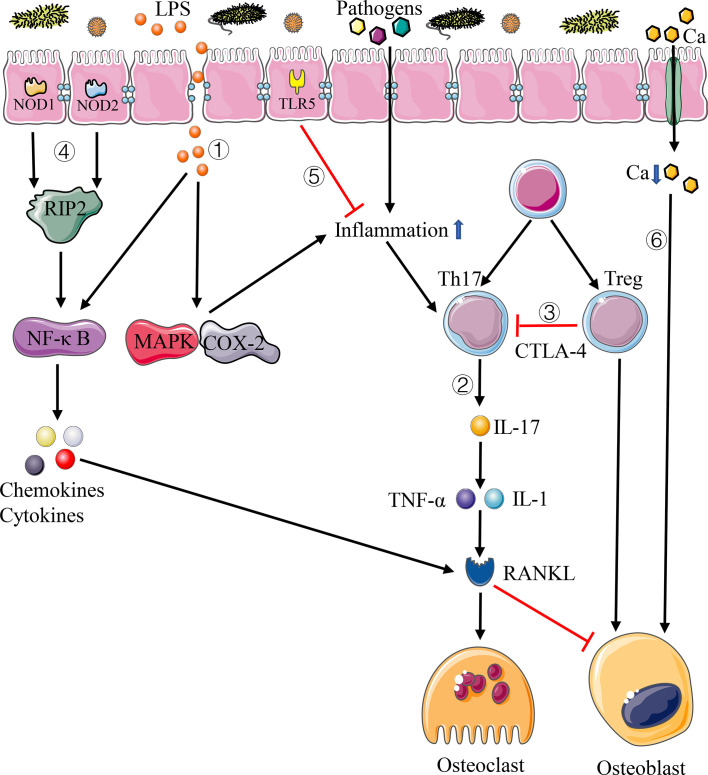
Figure 1.
Pathways of immune system affecting bone homeostasis. 1) Disturbance of intestinal flora increases the permeability of intestinal mucosal barrier, letting more LPS and pathogens into the circulation system, which can lead to systemic inflammation. 2) Th17 cells produce IL-17, resulting in the increase of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-1, thus enhancing the expression of RANKL. 3) Treg cells inhibit the activation of T cells through CTLA-4-mediated pathway, thus inhibiting the differentiation of osteoclasts. 4) NOD1 and NOD2 bind peptidoglycans on the surface of bacteria and activate the NF-κB pathway through RIP2, resulting in gene expression of chemokines and cytokines. 5) TLR5 binds with the flagellin of bacteria and inhibit the inflammation. 6) Disturbance of intestinal flora increases intestinal pH and decreases calcium absorption.