Figure 2.
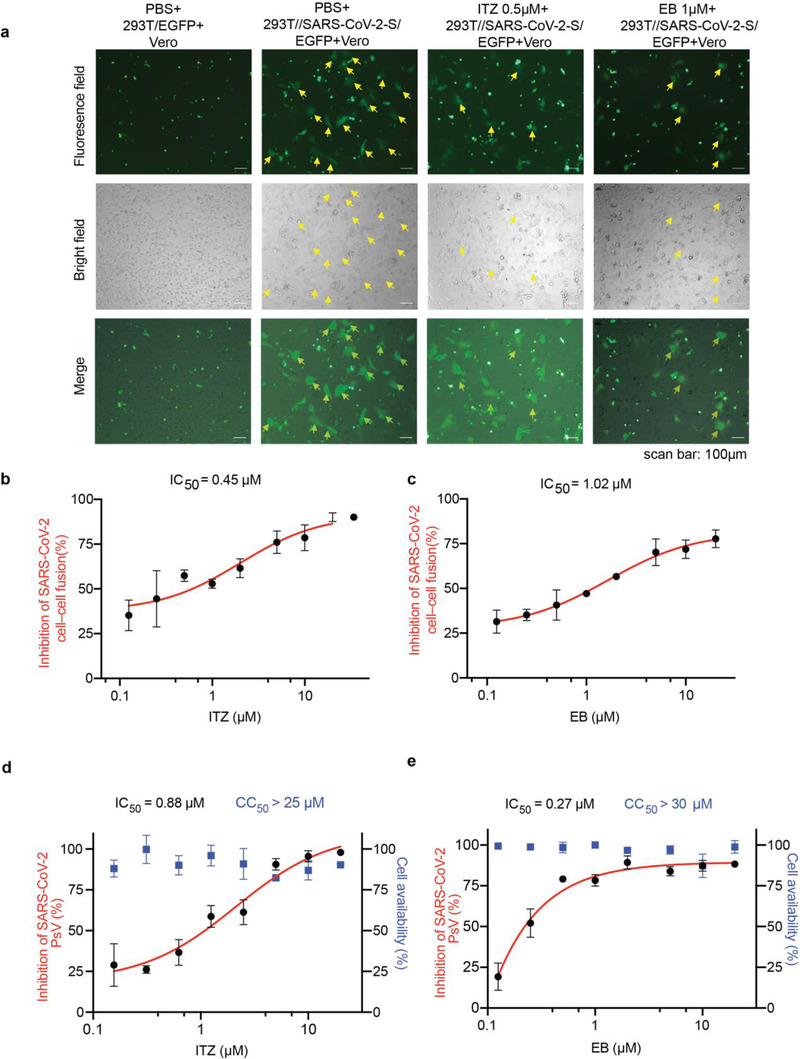
ITZ and EB inhibited SARS‐CoV‐2 infection via blocking spike protein‐mediated membrane fusion. a) Cell‐cell fusion mediated by SARS‐CoV‐2 S protein. ITZ and EB inhibited the SARS‐CoV‐2 S‐mediated syncytium formation on Vero cells at 24 h. 293T/EGFP, HEK‐293T cells transfected with vector (pAAV‐IRES‐EGFP), scale bars, 100 µm. b,c) Quantification of GFP‐positive syncytia. Three images per condition were acquired and processed. Data were normalized to PBS controls and depicted as fold changes in mean GFP expression. Dose‐response curves and IC50s of b) ITZ and c) EB on inhibiting SARS‐CoV‐2 S‐mediated syncytium formation. d,e) Inhibition of entry of SARS‐CoV‐2 PsV by d) ITZ and e) EB. SARS‐CoV‐2 PsV were pretreated with gradient concentrations of ITZ or EB, then inoculated with 293T‐ACE2 cells. The luciferase activity were measured 48 h post transduction. The blue squares indicate the percent cytotoxicity of the ITZ or EB. Results are representative of n = 3. All experiments were done in triplicates and repeated three times, data are expressed as means ± S.D.(error bar).
