Figure 3.
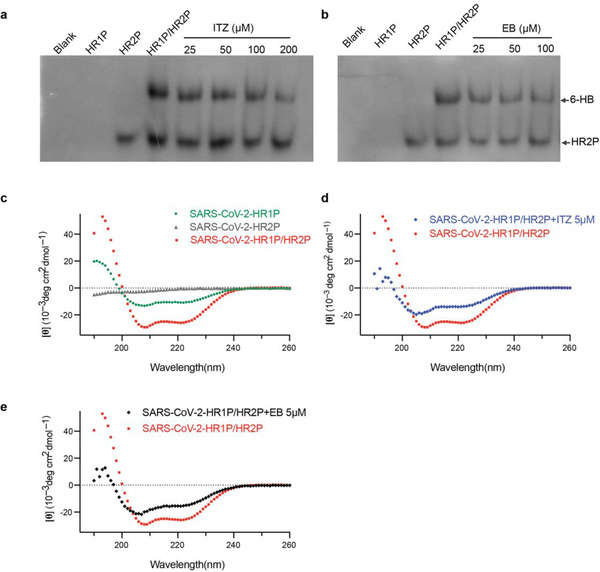
Molecular mechanism of ITZ and EB for inhibiting SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. a,b) Dose‐dependent inhibition of 6‐HB formation by ITZ (a) and EB (b), as assesed by N‐PAGE. HR1P (lane 2) were prtreated with indicated concentration of ITZ or EB, followed by the addition of HR2P (lane 3). ITZ (a, lane 4–8) or EB (b, lane 4–7) inhibit the 6‐HB (upper part) formation between HR1P and HR2P. c‐e) ITZ and EB interfered the formation of 6‐HB, as analysed using CD spectroscopy. The CD profile of HR1P/HR2P mixture (10µM) showed the characteristic α‐helical spectrum with double minima peak at 208 and 222 nm (c). With the addition of ITZ (d) or EB (e), the secondary structures of 6‐HB in HR1P/HR2P mixture were affected, showing a lower α‐helicity.
