Figure 4.
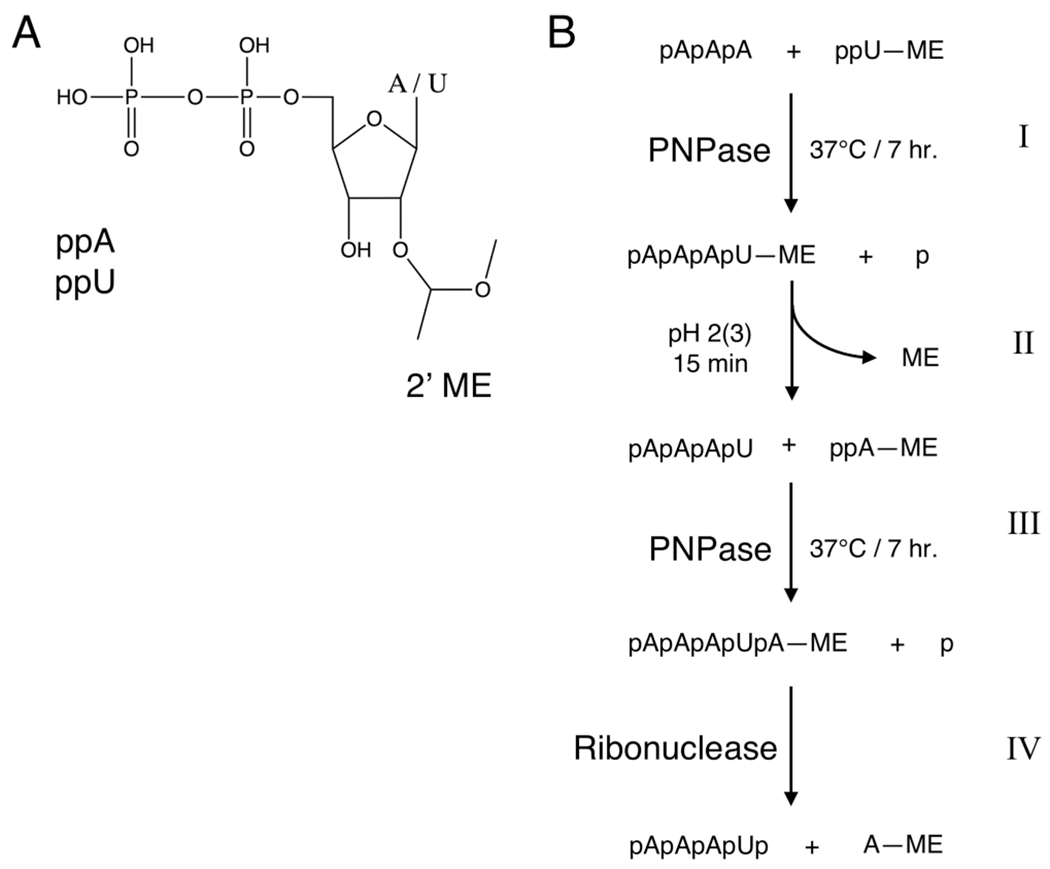
PNPase synthesis of polyribonucleotides of defined sequence. (A) Ribonucleotide representation, either adenosine (A) or uridine (U), diphosphate (pp), with 2′ (3′)-O-(α-methoxyethyl) blocking group (ME). (B) Solution-phase enzymatic RNA synthesis with 2′-protected ribonucleotides. (I) Adenosine trinucleotide (initiator) is coupled to 5′ diphosphate uridine protected at the 2′ position with α-methoxyethyl in the presence of PNPase at 37 °C for 7 h to generate 2′-protected tetranucleotide. (II) The α-methoxyethyl protecting group is removed with acid [pH 2 (3) for 15 min]. (III) The next nucleotide, 2′-protected 5′ ADP, is coupled to the tetranucleotide initiator (conditions are the same as those in step I). (IV) The structure of a blocked pentanucleotide is then confirmed by hydrolysis with pancreatic ribonuclease.
