Figure 5.
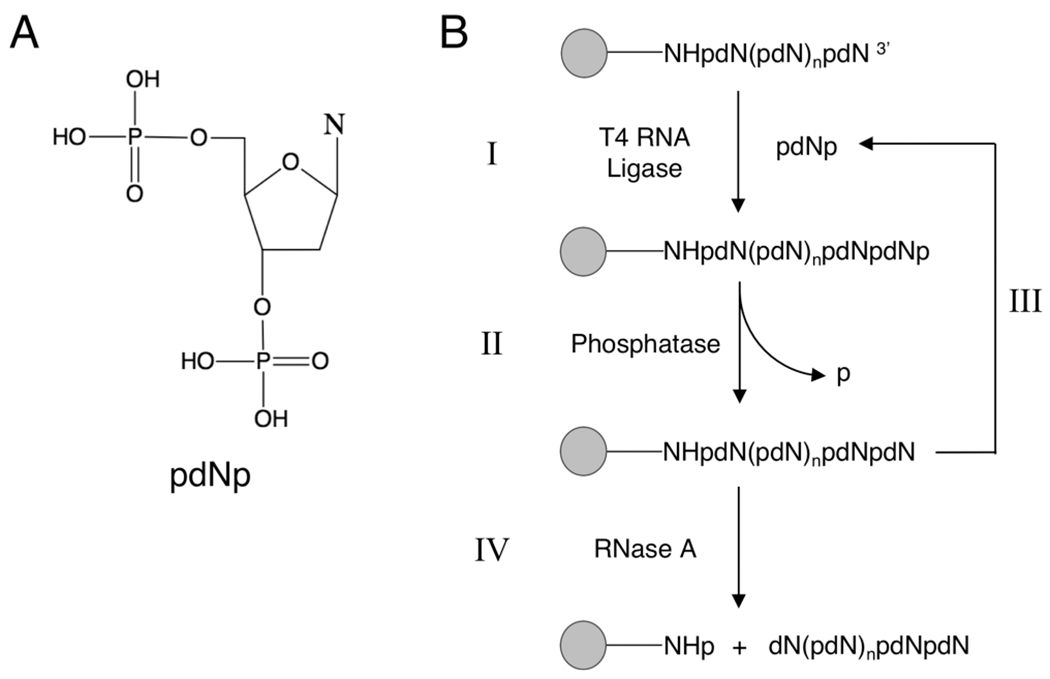
Solid-phase T4 RNA ligation of bisphosphate monomers to generate ssDNA. (A) Structure of 5′, 3′ bisphosphate-2′-deoxynucleoside (pdNp), where dN is any 2′ deoxynucleoside (A, G, C, or T). (B) Enzymatic synthesis performed in the solid phase, where 5′-phosphorylated initiator is covalently attached to Tentagel. (I) pdNp is ligated to the initiator at the 3′ hydroxyl in the presence of T4 RNA ligase. (II) The 3′ phosphate (p) is removed with alkaline phosphatase. (III) The process is repeated until the full-length product is established. (IV) The target strand is enzymatically released from the support with RNase A, yielding 5′, 3′ dephosphorylated product.
