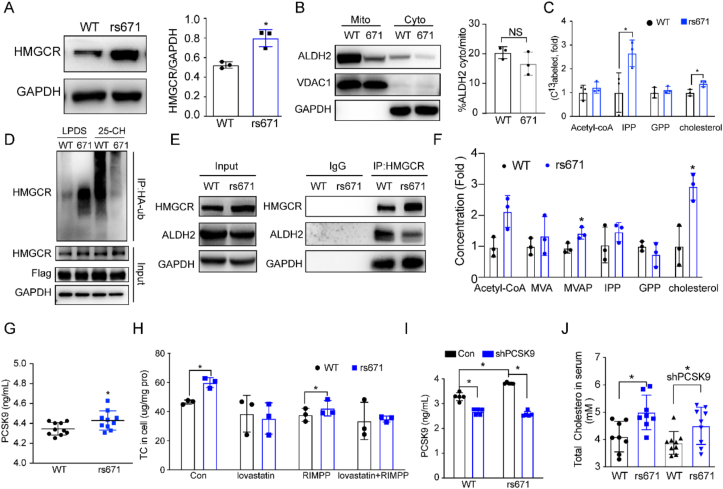
Fig. 7.
ALDH2 rs671 (ALDH2*2) mutant increases cholesterol synthesis primarily through decreasing HMGCR degradation. (A) Representative image and quantification of HMGCR expression in wild type ALDH2 (WT) and ALDH2*2 (671) primary mouse hepatocytes (n = 3). (B) Wild type ALDH2 (WT) and ALDH2*2 (671) expression in mitochondria and cytoplasm (n = 3). (C) 13C-acetate incorporation into cholesterol in WT and ALDH2*2 hepatocytes (n = 3). (D) HMGCR ubiquitination is diminished in rs671 cells stimulated with 25-HC compared to WT. (E) HMGCR is stabilized in rs671 human liver tissues (n = 3). (F) Major intermediates in de novo cholesterol synthesis in WT and ALDH2 rs671 human liver tissues (n = 5). (G) PCSK9 concentrations in 13-week old mouse serum after Western diet feeding for 7 weeks (n = 10). (H) GC-MS analysis of total cholesterol in hepatocytes treated with RIMPP or lovastatin (n = 3). (I) PCSK9 levels in mice injected with control or shPCSK9 AAV (n = 9). (J) Total cholesterol concentration in mouse serum after Western diet feeding for 9 weeks (n = 8–9). Statistical comparisons were made using a 2-tailed Student's t-test or ANOVA. All data are mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.