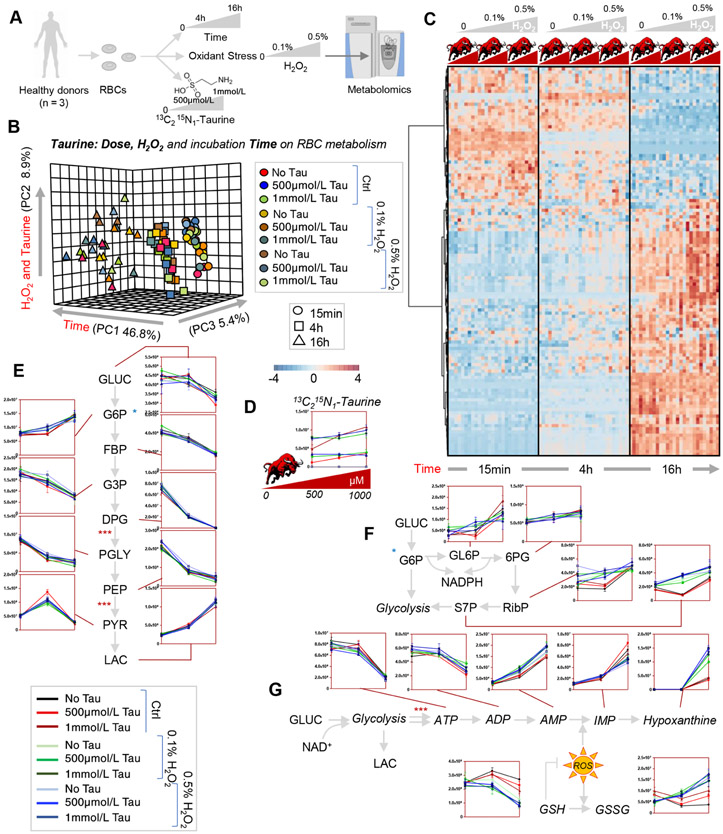
Fig. 4.
Tracing experiments with 13C15N-taurine in human RBCs further confirm a role in protection from H2O2-induced oxidant stress to GSH and purines. Human RBCs (n = 3) were incubated with 500 μmol/L or 1 mmol/L for 15 minutes and 4 and 16 hours, in the absence of stress or in presence of oxidant stress with hydrogen peroxide (either 0.1% or 0.5%, A). In B and C, results from the PLS-DA and hierarchical clustering analysis of the significant metabolites by repeated-measures two-way ANOVA. While no labeled catabolites of stable isotope-labeled taurine were detected in this study (D), and time was the major factor contributing to the observed alteration in glycolysis (E), this analysis confirmed a protective role of higher concentrations of taurine against oxidant stress, resulting in decreased activation of the pentose phosphate pathway (F) and better preservation of the GSH system and nonoxidized purines (G). Y axes in line plots are shown as arbitrary units (E-G).