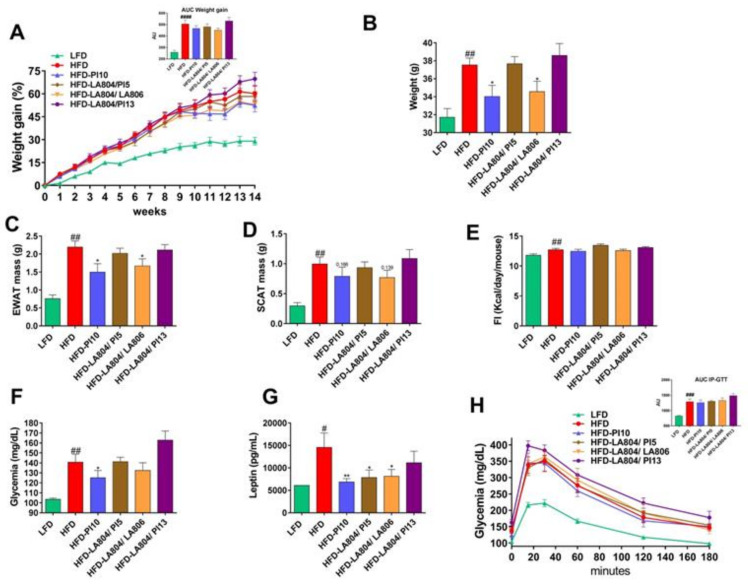
Figure 4.
B. longum PI10 and the B. animalis subsp. lactis LA804/L. gasseri LA806 mixture limited high-fat diet (HFD)-induced body weight gain, fat mass increase, hyperglycemia, and hyperleptinemia but had no impact on HFD-induced glucose intolerance. (A) Evolution of body weight gain (in %) in mice receiving probiotics or excipient and fed a low-fat diet (LFD) or HFD for 14 weeks and the corresponding area under the curve (AUC) (in arbitrary unit [AU]). (B) Body weight at sacrifice (in g). (C) Epididymal adipose tissue (EWAT) mass at sacrifice (in g). (D) Subcutaneous adipose tissue (SCAT) mass at sacrifice (in g). (E) Cumulative food intake (in kcal/day/mouse). (F) Fasting blood glucose levels at 13 weeks of diet (in mg/dL). (G) Fasting blood leptin level at 13 weeks of diet (in pg/mL). (H) Intra-peritoneal glucose tolerance test (IP-GTT) at 12 weeks of diet and the corresponding AUC (in AU). Blood glucose levels (mg/dL) measured after intraperitoneal glucose injection. Data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. of 4 (LFD) to 8 (HFD) mice per group. # corresponds to diet effect (HFD vs. LFD), * corresponds to treatment effect (Probiotic vs. Excipient). * or # p < 0.05, ** or ## p < 0.01; ### p < 0.001; #### p < 0.0001.