Figure 33.
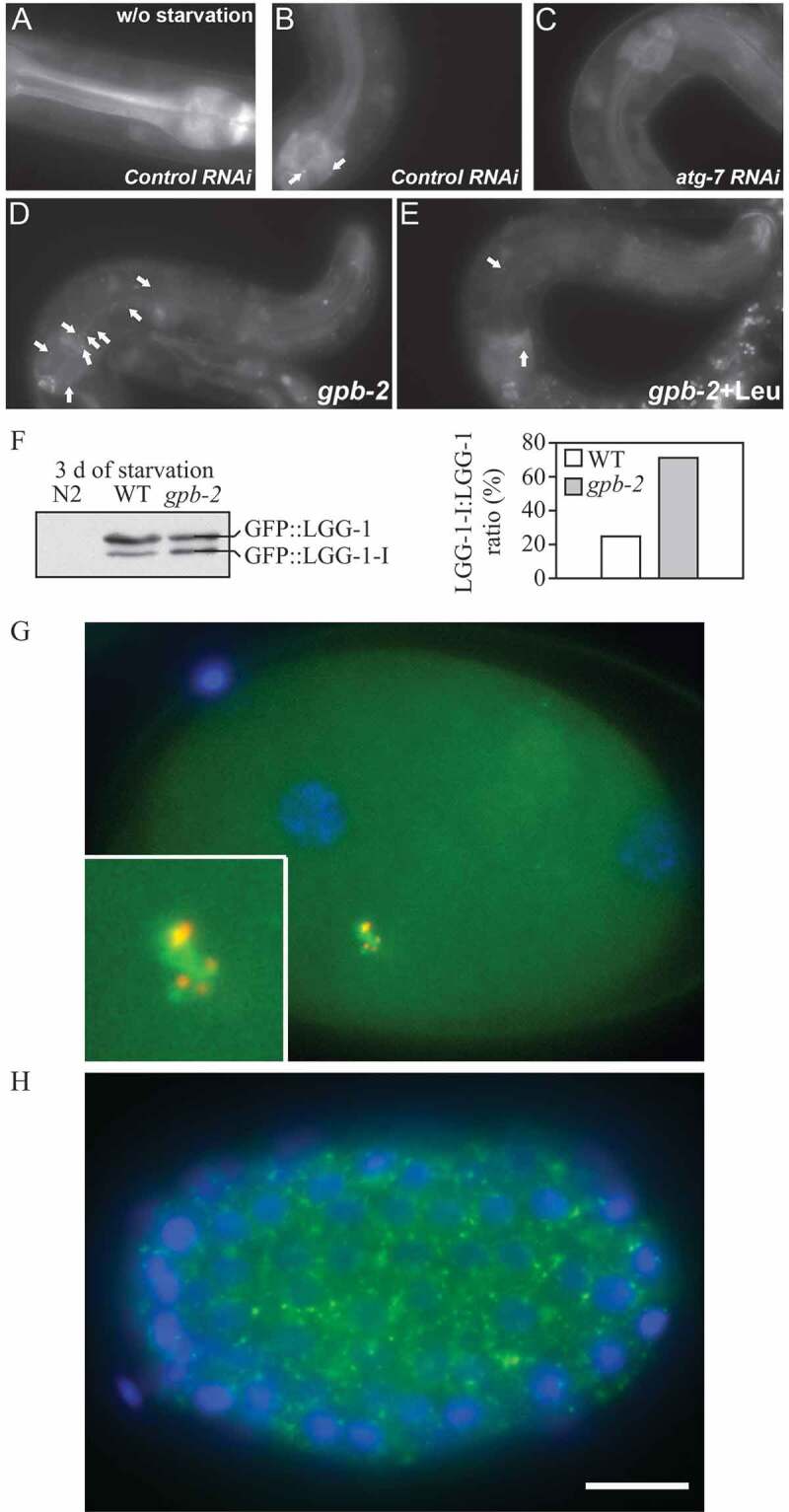
GFP::LGG-1 and GFP::LGG-2 are autophagy markers in C. elegans. (A-F) Animals were generated that carry an integrated transgene expressing a GFP-tagged version of lgg-1, the C. elegans ortholog of mammalian MAP1LC3. Representative green fluorescence images in the pharyngeal muscles of (A) control RNAi animals without starvation, (B) control RNAi animals after 9 d of starvation, (C) atg-7 RNAi animals after 9 d of starvation, (D) starvation-hypersensitive gpb-2 mutants without leucine after 3 d of starvation, and (E) gpb-2 mutants with leucine after 3 d of starvation. The arrows show representative GFP::LGG-1-positive punctate areas that label pre-autophagosomal and autophagosomal structures. (F) The relative levels of PE-conjugated and unconjugated GFP::LGG-1 were determined by western blotting. These figures were modified from data previously published in ref. [2115], Kang, C., Y.J. You, and L. Avery. 2007. Dual roles of autophagy in the survival of C. elegans during starvation. Genes & Development. 21:2161-2171, Copyright © 2007, Genes & Development by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, and ref. [4086], Kang, C., and L. Avery. 2009. Systemic regulation of starvation response in C. elegans. Genes & development. 23:12-17, Copyright © 2011, Genes & Development by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, www.genesdev.org. (G-H) GFP:LGG-2 serves as a marker for autophagosomes in early C. elegans embryos. (G) GFP::LGG-2 expressed in the germline from an integrated transgene reveals the formation of autophagosomes (green) around sperm-inherited membranous organelles (red). DNA of the two pronuclei is stained (blue). (H) Later during development, GFP::LGG-2-positive structures are present in all cells of the embryo. Scale bar: 10 µm. Images provided by V. Galy
