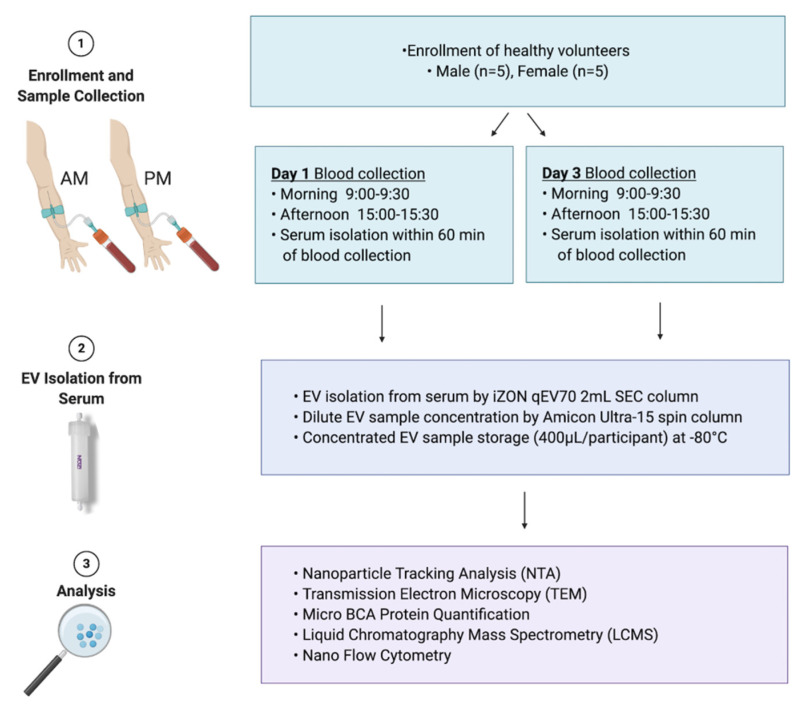
Figure 1.
Study design. A cohort of healthy males and females aged 18 to 65 years were recruited (n = 10) for extracellular vesicle variability study (EVV). Blood was collected in the morning (AM) and the afternoon (PM) on day 1 and day 3 of the study. Participants were fed on day 1 and fasted on day 3 for morning blood collection. Serum was isolated from whole blood and used for extracellular vesicles (EV) isolation. EVs were isolated using qEV70 2 mL SEC column, concentrated to the volume of 400 µL in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and used for downstream analyses. These included nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) to determine EV concentration/yield, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) for EV size estimations and morphology assessment, microBCA protein quantification, liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS) for EV protein quantification, and nano flow cytometry for EV surface marker characterisation (EV-TRACK ID: EV210044).