Fig. 7.
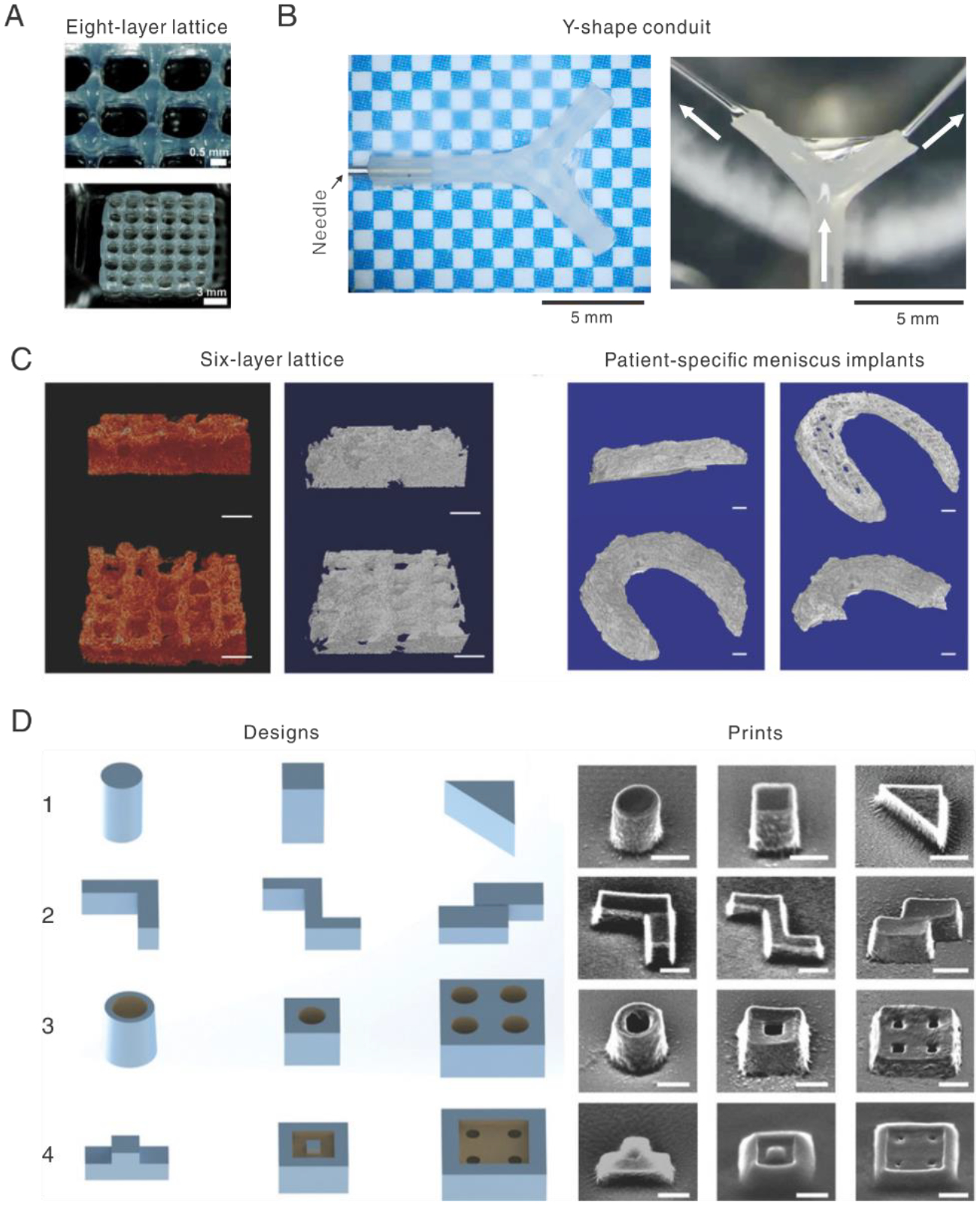
Typical 3D prints with silk-based inks. A. Eight-layer lattice scaffold printed with recombinant spider silk. [49], Copyright 2015. Reprinted with permission from the John Wiley and Sons. B. Y-shape conduit printed with regenerated silk fibroin without using sacrificial or supporting materials. Water jet from the silk conduit, indicated by white arrows, demonstrates the remarkable strength and perfusability. [40], Copyright 2020. Reprinted with permission from the John Wiley and Sons. C. Micro-CT images of enzyme-crosslinked silk prints after freeze-drying. Scale bars: left, 1 mm; right 2.5 mm. [211], Copyright 2017. Reprinted with permission from the John Wiley and Sons. D. Left, a set of designs; right, corresponding SEM images of silk structures by ion and electron beam lithography. The scale bar is 500 nm. [240], Copyright 2018. Reprinted with permission from the John Wiley and Sons.
