Table 1.
Main properties and structures of inorganic nanoparticles (NPs).
| Inorganic NPs | Properties | Structure | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gold NPs | High surface to volume ratio, easy functionalization with antibodies, suitable for passive and active targeting, near infrared absorption, localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) characteristics |  |
[34] |
| Magnetic NPs | Selective destruction of cancer cells due to heat release, superparamagnetism, and high field irreversibility |  |
[35] |
| Carbon-based NPs | High strength, electron affinity, water solubility, and biocompatibility |  |
[36,37] |
| Quantum dots | Broad excitation and narrow emission spectra, with high quantum yields and photostability |  |
[38] |
| Silica NPs | High biocompatibility and stability, with easy surface functionalization |  |
[28] |
| Upconversion NPs | Used for the treatment of deep-seated tumors and exhibit lower phototoxicity |  |
[28,39] |
| Ceramic NPs | Controlled release of drugs, easy incorporation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, with high loading capacity | 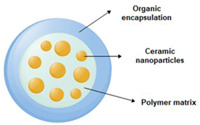 |
[40] |
