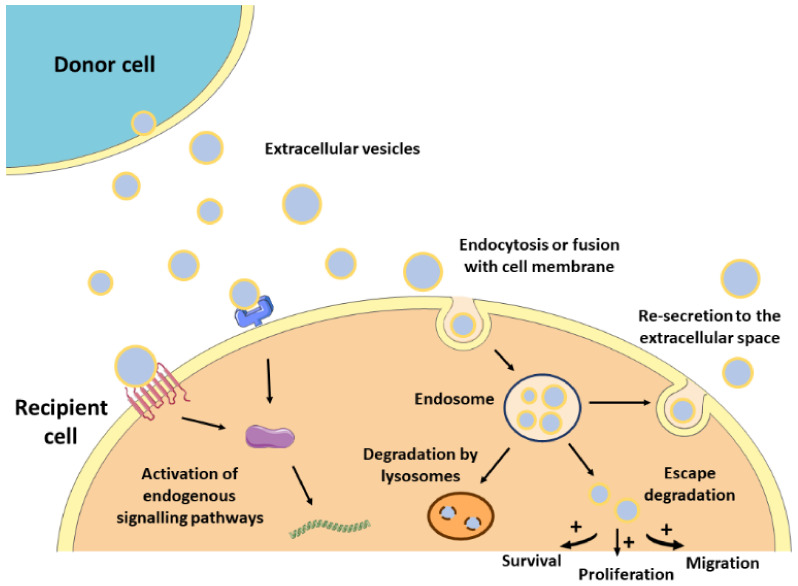
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of EVs. After released from donor cells, EVs may induce a response in recipient cells by different mechanisms. First, EVs may remain at the binding site on the cell membrane eliciting functional responses by activating downstream molecular pathways. Alternatively, EVs may be internalized by endocytosis or fusion with the cell membrane undergoing different intracellular fates. They can be targeted for degradation by lysosomes, they can escape degradation and modulate cell behavior, or they can be re-secreted to the extracellular space.