FIGURE 2. Controlled synthesis of gold-graphene hybrid nanomaterials.
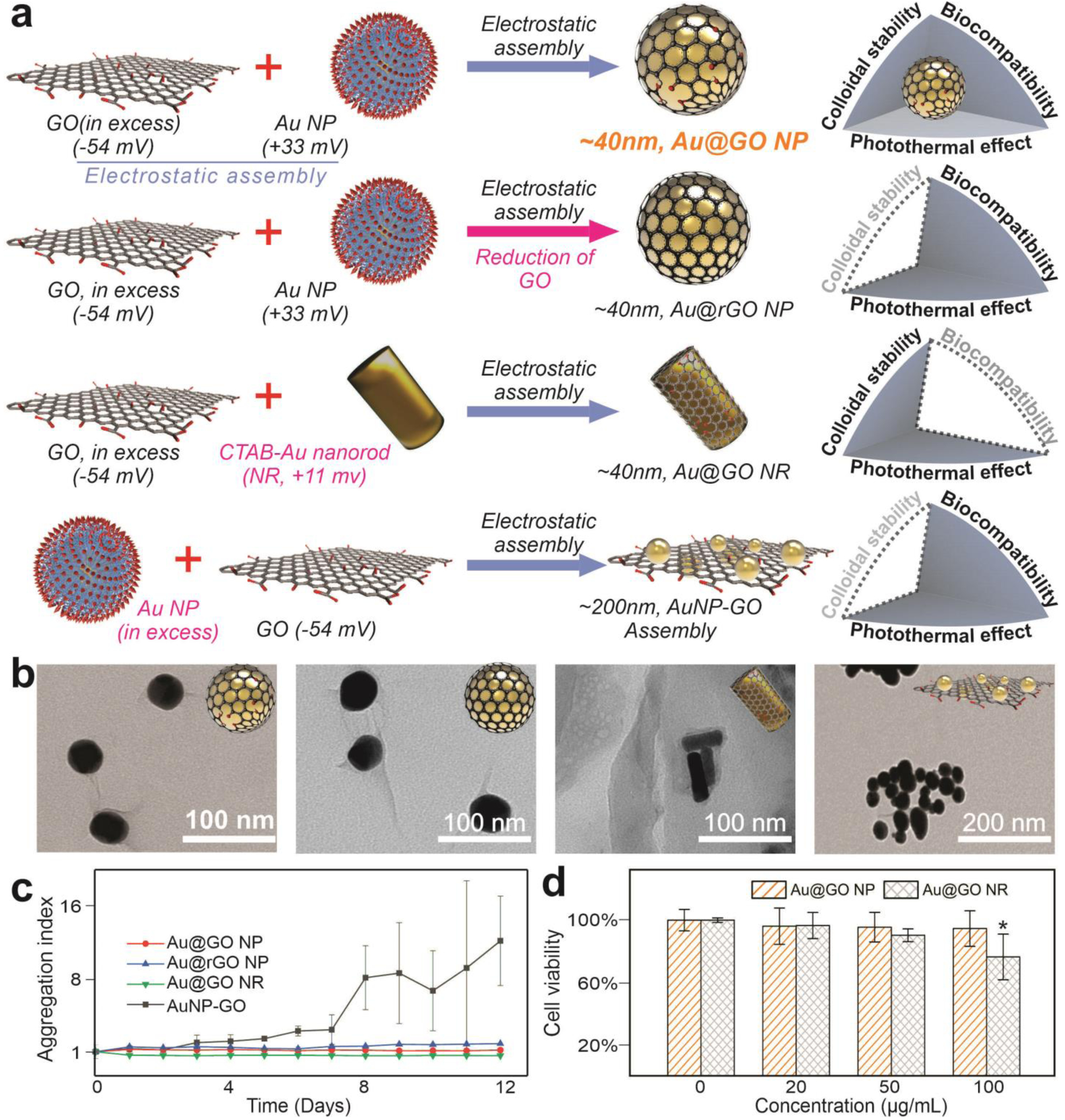
a) Schematic diagrams showing the controlled synthesis of varying differentially structured gold-graphene hybrid nanomaterials with distinct colloidal stability, biocompatibility, and capability of inducing photothermal hyperthermia. NP represents nanoparticles, RGO represents reduced graphene oxide, and NR represents nanorods. b) Representative transmission electron microscope (TEM) images showing the successfully synthesized graphene/gold hybrid nanoparticles. c) Higher colloidal stability of Au@GO NP and AuNR@GO compared to the Au@rGO NP based on a graph comparing the aggregation index of different structures of graphene/gold nanoparticles. d) A better biocompatibility of Au@GO NP compared to Au@GO NR based on a MTS assay and using cancer and fibroblast cell lines. The CTAB ligands in the Au NRs may contribute cytotoxicity of Au@GO NR. *P<0.05, by student’s t test. n=3 from independent experiments.
