FIGURE 5. Synergistic cancer therapeutics based on Au@GO NP-NAC-enabled chemo/gene therapy and NIR PT hyperthermia.
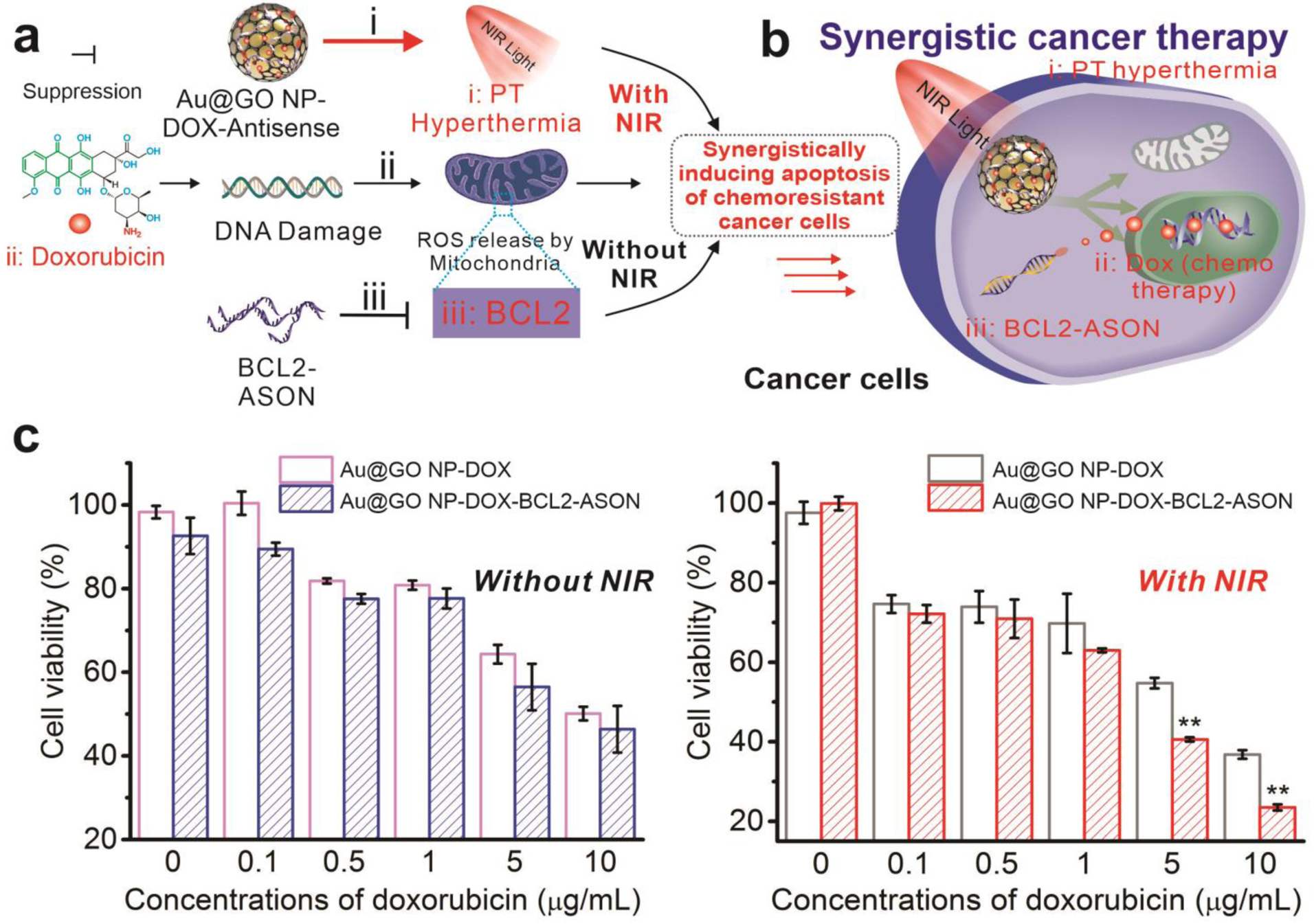
a) A schematic diagram depicting synergistic co-sensitization of cancer cells towards anti-cancer drug (DOX) through combined PT hyperthermia (NIR laser) treatment and BCL2-ASON delivery. b) The combined treatment mediated by Au@GO NP-NACs leads to synergistic cancer cell apoptosis. c) The cell viabilities of glioblastoma cells treated with the Au@GO NP carrying DOX only or both DOX and BCL2-ASON with or without NIR exposure. Without NIR irradiation (left), IC50 decreased from 10 μg/ml for Au@GO NP-DOX to around 6.7 μg/ml for Au@GO NP-DOX-BCL2-ASON. Through a further NIR irradiation, however, the IC50 of Au@GO NP-DOX-BCL2-ASON was decreased to 2.4 μg/ml. On the other hand, NIR irradiation only (Au@GO NP-DOX on the right) decreased the IC50 of DOX from 10 μg/ml to 5.4 μg/ml. The apoptotic assay together with the aforementioned gene pathway studies supported the hypothesis in (a) that cancer cells can be synergistically sensitized towards chemotherapy by the combination of PT hyperthermia and BCL2-ASON in a single platform through a collective effect on the intracellular apoptotic pathways in cancer cells. n=3 biological replicates. **P<0.01 (compared to the control) by student’s t-test.
