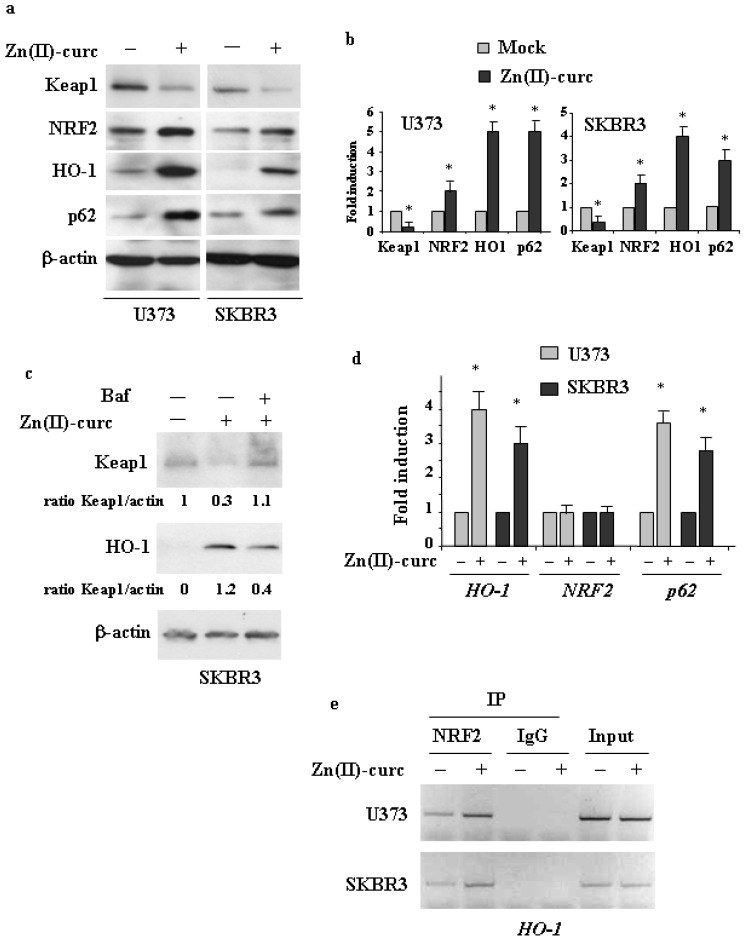
Figure 1.
Zn (II)–curc activates NRF2. (a) Western blot analysis of Keap1, NRF2, HO-1 and p62 protein levels in U373 and SKBR3 cells untreated or treated with Zn (II)–curc (100 μg/mL) for 24 h. (b) Densitometric analysis was performed using Image J software to calculate the ratio of the protein levels, as detected in (a), vs. β-actin, with the control set to 1. Histograms represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p ≤ 0.05. (c) Western blot analysis of Keap1 and HOI-1 in SKBR3 cells undergoing Bafilomycin A1 (BAF) (20 nM) treatment for 3 h followed by Zn (II)–curc (100 μg/mL) for 16 h. Anti-β-actin was used as protein loading control. (d) Total mRNA was extracted from U373 and HT29 cells untreated or treated with Zn (II)–curc (100 μg/mL) for 16 h. HO-1, Nrf2 and p62 gene expression was assayed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) of reverse-transcribed cDNA. Densitometric analysis was performed using Image J software to calculate the gene expression/28S ratio. Histograms represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p ≤ 0.05. (e) U373 and SKBR3 were treated with Zn–curc (100 μg/mL) for 16 h before being assayed for chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis (ChIP) with anti-NRF2 antibody. PCR analysis was performed on the immunoprecipitated protein/DNA complex using primers specific for HO-1 promoter. A sample representing linear amplification of the total chromatin (input) was included as control. Additional controls included immunoprecipitation performed with non-specific immunogloblulins (IP: IgG).