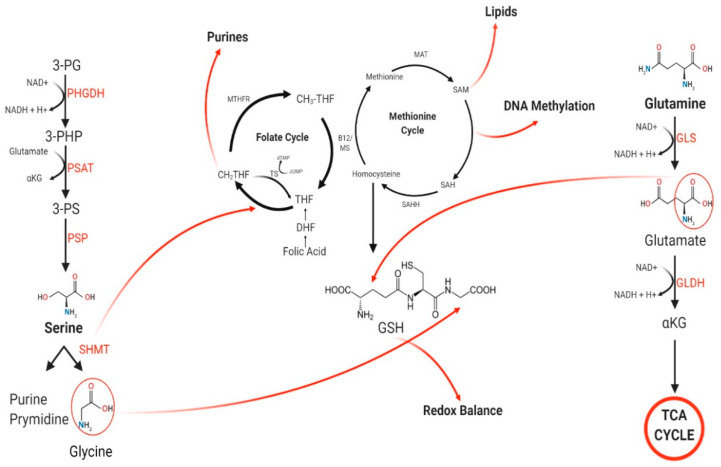
Figure 1.
Schematic of the interaction between the three metabolic pathways (serine biosynthesis, 1-C metabolism, and glutamine metabolism). Serine is synthesized from 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PG) by phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH), phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT), and phosphoserine phosphatase (PSP). Serine is further converted to glycine by SHMT, which donates a carbon to the folate cycle. Tetrahydrofolate (THF) is converted to CH3THF by TS and MTHFR to complete the folate cycle. During demethylation of CH3THF, a carbon is donated to the methionine cycle by Vitamin B12. Methionine is synthesized to homocysteine by methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) and SAAH, producing S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). Glutamine is converted to glutamate by the enzyme glutaminase. The side chain of glutamate is then used to form GSH. Abbreviations 3-PG—3-phosphoglycerate; PHGDH— phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PSAT—phosphoserine aminotransferase; 3-PHP—3-phosphohydroxypyruvate; 3-PS—3-phosphoserine; PSP—phosphoserine phosphatase; SHMT—serine hydroxymethyltransferase; TS—Thymidylate Synthase; dUMP—deoxyuridine monophosphate; dTMP—deoxythymidine monophosphate; MTHFR—methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; THF—tetrahydrofolate; CH3THF—5-methyltetrahydrofolate; CH2THF—5,10-methylene-THF; B12—Vitamin B12; MS—Methionine synthase; MAT—Methionine adenyltransferase; SAM—S-adenosylmethionine; SAH—S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAHH—S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase; GSH—Glutathione; GLS—Glutaminase; GLDH—Glutamate dehydrogenase; TCA—tricarboxylic acid. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 16 February 2021).