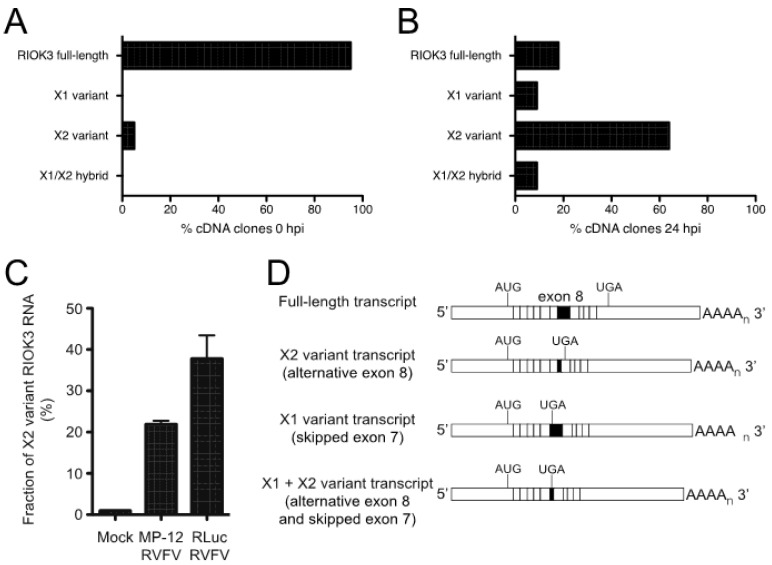
Figure 3.
RVFV infection induces alternative splicing of RIOK3 transcripts. Distribution of RIOK3 splicing isoforms in either mock-infected (A) or rLuc RVFV infected (B) HEK293 cells. Total RNA was purified from mock- or virus-infected cells, reverse transcribed/PCR amplified into mRNA-length cDNAs, and cloned in a plasmid. From each sample, 40 individual clones were sequenced and categorized as full length, X1, X2, or X1/X2 hybrid. (C) Prevalence of RIOK3 X2 alternative splicing in infected cells. HEK293 cells were infected (MOI 1.0) with either MP-12 or rLuc RVFV and total RNA was extracted after 24 h. The fraction of X2 variant alternative splicing was quantified by RT-qPCR using primers specific to detect the canonical and X2 isoforms at exons 8 and 9, and not necessarily in full length poly-adenylylated mRNAs, which were characterized in panels (A,B). Data in panel C is presented as mean +/− SEM from triplicate experiments. (D) Schematic of the different splicing patterns observed. X2 employs a cryptic splice donor site within exon 8, resulting in a shortened exon 8 and a new stop codon in exon 9. X1 skips exon 7 entirely. Some transcripts contained both X1 and X2 type alternative splicing.