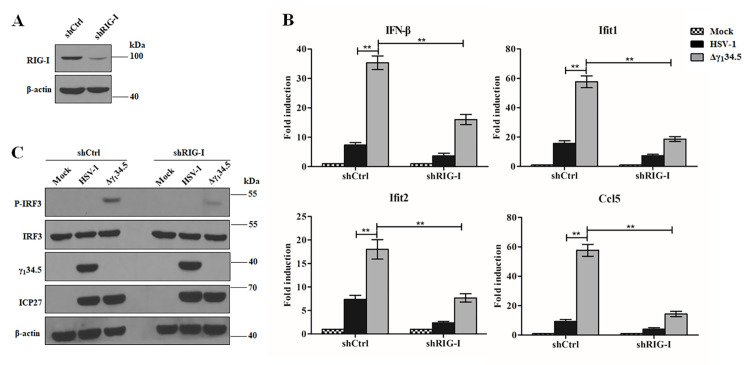
Fig 3. HSV-1 γ134.5 reduces RIG-I dependent antiviral responses in human lung fibroblasts (HEL).
(A) Validation of RIG-I knockdown in HEL cells. Cell lysates from HELs expressing control shRNA (shCtrl) or RIG-I target shRNA (shRIG-I) were subjected to western blot analysis with anti-RIG-I and β-actin antibodies. (B) Effects of γ134.5 on antiviral gene expression in control or RIG-I knockdown HEL cells. Cells infected with wild type HSV-1 or Δγ134.5 (5 pfu/cell) for 8 h were analyzed for transcript levels of IFN-β, Ifit1, Ifit2, and Ccl5 by quantitative PCR analysis. The data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA (**, P < 0.01) with SD (n = 3). (C) Effects of γ134.5 on IRF3 phosphorylation in shCtrl-transfected HEL or RIG-I knockdown HEL. Cells were infected as described in panel B and processed for Western blot analysis with antibodies against p-IRF3, IRF3, ICP27, γ134.5 and β-actin. The experimental data are representative of results from three independent experiments.