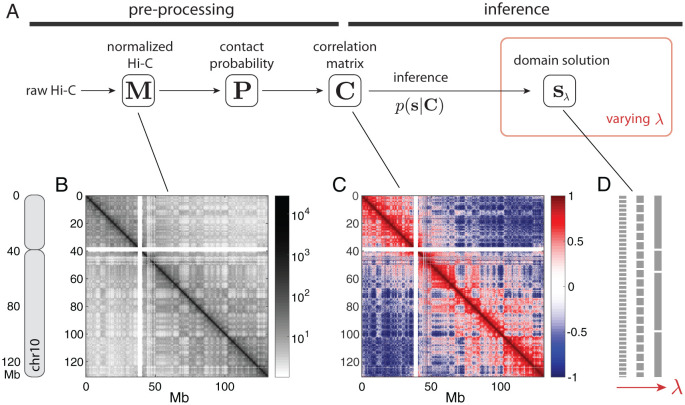
Fig 2. An overview of the Multi-CD method.
(A) We first pre-process Hi-C data to extract a correlation matrix C. Given C, we infer the chromatin domain (CD) solutions s at multiple scales by varying a single parameter λ. At each λ, the best domain solution is found through simulated annealing, in which the effective temperature T is gradually decreased (inner blue box). A complete Multi-CD algorithm involves repeating the process for different values of λ (outer red box), to obtain a family of solutions. (B) An example of the normalized Hi-C matrix, (C) and the correlation matrix that results from pre-processing. Shown is the full chromosome 10 in GM12878 (50-kb Hi-C), which is used as an example dataset throughout the paper. (D) Simplified schematic for the resulting family of domain solutions, {sλ}, at varying parameter λ. Each s is a vector of domain indices; line breaks illustrate domain boundaries. These solutions are not meant to be the optimal solutions for the shown data, but they illustrate how the typical domain scale increases with λ.