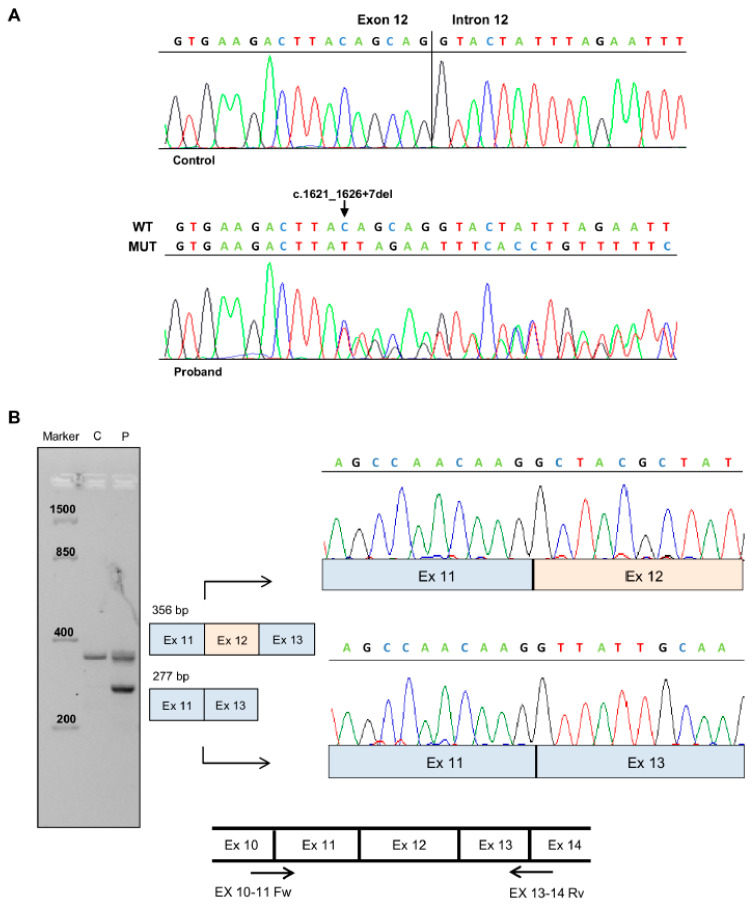
Figure 2.
Characterization of APC splicing mutation c.1626_1627+7del. (A) Sequencing electropherograms of genomic DNA from a healthy control individual and the proband, showing the splicing mutation c.1626_1627+7del. (B) Left: Agarose gel electrophoresis showing the RT-PCR analysis of mRNA extracted from peripheral blood of the patient (P) carrying the APC c.1621_1626+7del mutation and a healthy control (C). Amplified products obtained with primers spanning APC exon 10–11 and 13–14 boundaries were separated on 3% agarose gel and independently sequenced. Center: Schematic diagrams showing the wild type amplification product (356 bp) and the altered-splicing amplification product lacking APC exon 12 (277 bp). Right: Sequencing electropherograms of cDNA splicing isoforms generated from the wild type and mutant RT-PCR products. Bottom: Diagram showing the localization of the primers (indicated as arrows) used for RT-PCR experiments.