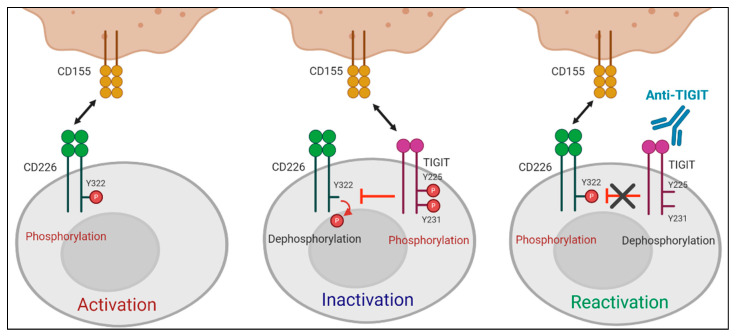
Figure 2.
Role of CD226 in anti-TIGIT immunotherapy. TIGIT has a direct effect on intracellular regulation of CD226 activation in response to PVR binding. (Left) When TIGIT expression is absent or low, engagement of CD226 with PVR induces the phosphorylation of tyrosine 322 (Y322) on CD226, which leads to the activation of intracellular signaling cascades. (Middle) PVR preferentially binds to upregulated TIGIT over CD226. Upon interaction with PVR, the cytoplasmic tail of TIGIT is phosphorylated. This PVR-induced TIGIT phosphorylation inhibits T cell responses by promoting CD226 dephosphorylation. (Right) TIGIT blockade suppresses PVR-induced TIGIT phosphorylation and restores the impaired Y322 phosphorylation of CD226, thereby leading to T cell activation.